Lymph node-resident lymphatic endothelial cells mediate peripheral tolerance via Aire-independent direct antigen presentation
- PMID: 20308365
- PMCID: PMC2856027
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20092465
Lymph node-resident lymphatic endothelial cells mediate peripheral tolerance via Aire-independent direct antigen presentation
Abstract
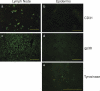
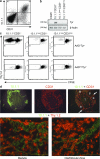
Peripheral immune tolerance is generally thought to result from cross-presentation of tissue-derived proteins by quiescent tissue-resident dendritic cells to self-reactive T cells that have escaped thymic negative selection, leading to anergy or deletion. Recently, we and others have implicated the lymph node (LN) stroma in mediating CD8 T cell peripheral tolerance. We demonstrate that LN-resident lymphatic endothelial cells express multiple peripheral tissue antigens (PTAs) independent of the autoimmune regulator (Aire). They directly present an epitope derived from one of these, the melanocyte-specific protein tyrosinase, to tyrosinase-specific CD8 T cells, leading to their deletion. We also show that other LN stromal subpopulations express distinct PTAs by mechanisms that vary in their Aire dependence. These results establish lymphatic endothelial cells, and potentially other LN-resident cells, as systemic mediators of peripheral immune tolerance.
Figures


Comment in
-
Immune tolerance: New peacekeepers identified.Nat Rev Immunol. 2010 May;10(5):290. doi: 10.1038/nri2766. Nat Rev Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20425917 No abstract available.
References
-
- Belz G.T., Behrens G.M., Smith C.M., Miller J.F., Jones C., Lejon K., Fathman C.G., Mueller S.N., Shortman K., Carbone F.R., Heath W.R. 2002. The CD8α+ dendritic cell is responsible for inducing peripheral self-tolerance to tissue-associated antigens. J. Exp. Med. 196:1099–1104 10.1084/jem.20020861 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Colella T.A., Bullock T.N.J., Russell L.B., Mullins D.W., Overwijk W.W., Luckey C.J., Pierce R.A., Restifo N.P., Engelhard V.H. 2000. Self-tolerance to the murine homologue of a tyrosinase-derived melanoma antigen: implications for tumor immunotherapy. J. Exp. Med. 191:1221–1232 10.1084/jem.191.7.1221 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

