The M230L nonnucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor resistance mutation in HIV-1 reverse transcriptase impairs enzymatic function and viral replicative capacity
- PMID: 20308384
- PMCID: PMC2876396
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.01795-09
The M230L nonnucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor resistance mutation in HIV-1 reverse transcriptase impairs enzymatic function and viral replicative capacity
Abstract
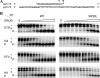
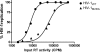
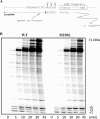
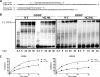
The M230L mutation in HIV-1 reverse transcriptase (RT) is associated with resistance to first-generation nonnucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NNRTIs). The present study was designed to determine the effects of M230L on enzyme function, viral replication capacity (RC), and the extent to which M230L might confer resistance to the second-generation NNRTI etravirine (ETR) as well as to the first-generation NNRTIs efavirenz (EFV) and nevirapine (NVP). Phenotyping assays with TZM-bl cells confirmed that M230L conferred various degrees of resistance to each of the NNRTIs tested. Recombinant viruses containing M230L displayed an 8-fold decrease in RC compared to that of the parental wild-type (WT) virus. Recombinant HIV-1 WT and M230L mutant RT enzymes were purified; and both biochemical and cell-based phenotypic assays confirmed that M230L conferred resistance to each of EFV, NVP, and ETR. RT that contained M230L was also deficient in regard to each of minus-strand DNA synthesis, both DNA- and RNA-dependent polymerase activities, processivity, and RNase H activity, suggesting that this mutation contributes to diminished viral replication kinetics.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Differential impact of the HIV-1 non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor mutations K103N and M230L on viral replication and enzyme function.J Antimicrob Chemother. 2010 Nov;65(11):2291-9. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkq338. Epub 2010 Sep 18. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2010. PMID: 20852269
-
Altered viral fitness and drug susceptibility in HIV-1 carrying mutations that confer resistance to nonnucleoside reverse transcriptase and integrase strand transfer inhibitors.J Virol. 2014 Aug;88(16):9268-76. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00695-14. Epub 2014 Jun 4. J Virol. 2014. PMID: 24899199 Free PMC article.
-
Role of the K101E substitution in HIV-1 reverse transcriptase in resistance to rilpivirine and other nonnucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2013 Nov;57(11):5649-57. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01536-13. Epub 2013 Sep 3. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2013. PMID: 24002090 Free PMC article.
-
HIV-1 reverse transcriptase connection subdomain mutations involved in resistance to approved non-nucleoside inhibitors.Antiviral Res. 2011 Nov;92(2):139-49. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2011.08.020. Epub 2011 Aug 28. Antiviral Res. 2011. PMID: 21896288 Review.
-
[Etravirine: genetic barrier and resistance development].Enferm Infecc Microbiol Clin. 2009 Dec;27 Suppl 2:32-9. doi: 10.1016/S0213-005X(09)73217-3. Enferm Infecc Microbiol Clin. 2009. PMID: 20116626 Review. Spanish.
Cited by
-
Novel Mutations L228I and Y232H Cause Nonnucleoside Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitor Resistance in Combinational Pattern.AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 2016 Sep;32(9):909-17. doi: 10.1089/AID.2015.0359. Epub 2016 May 9. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 2016. PMID: 27067022 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of the W153L substitution in HIV reverse transcriptase on viral replication and drug resistance to multiple categories of reverse transcriptase inhibitors.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2014 Aug;58(8):4515-26. doi: 10.1128/AAC.02729-14. Epub 2014 May 27. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2014. PMID: 24867966 Free PMC article.
-
Deep sequencing of HIV-1 near full-length proviral genomes identifies high rates of BF1 recombinants including two novel circulating recombinant forms (CRF) 70_BF1 and a disseminating 71_BF1 among blood donors in Pernambuco, Brazil.PLoS One. 2014 Nov 17;9(11):e112674. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0112674. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25401747 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of the E138K resistance mutation in HIV-1 reverse transcriptase conferring susceptibility to etravirine in B and non-B HIV-1 subtypes.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2011 Feb;55(2):600-7. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01192-10. Epub 2010 Dec 6. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2011. PMID: 21135184 Free PMC article.
-
Current perspectives on HIV-1 antiretroviral drug resistance.Viruses. 2014 Oct 24;6(10):4095-139. doi: 10.3390/v6104095. Viruses. 2014. PMID: 25341668 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Antela, A., J. Casado, A. Moreno, F. Dronda, M. Perez-Elias, and S. Moreno. 2001. Clinical relevance of the m230l mutation in the reverse transcriptase gene in patients rescued with a regimen including NNRTIs, abstr. 571. 1st IAS Conf. HIV Pathog.
-
- Arion, D., N. Kaushik, S. McCormick, G. Borkow, and M. A. Parniak. 1998. Phenotypic mechanism of HIV-1 resistance to 3′-azido-3′-deoxythymidine (AZT): increased polymerization processivity and enhanced sensitivity to pyrophosphate of the mutant viral reverse transcriptase. Biochemistry 37:15908-15917. - PubMed
-
- Arts, E. J., X. Li, Z. Gu, L. Kleiman, M. A. Parniak, and M. A. Wainberg. 1994. Comparison of deoxyoligonucleotide and tRNA(Lys-3) as primers in an endogenous human immunodeficiency virus-1 in vitro reverse transcription/template-switching reaction. J. Biol. Chem. 269:14672-14680. - PubMed
-
- Azijn, H., I. Tirry, J. Vingerhoets, M. P. de Bethune, G. Kraus, K. Boven, D. Jochmans, E. Van Craenenbroeck, G. Picchio, and L. T. Rimsky. 2010. TMC278, a next-generation nonnucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor (NNRTI), active against wild-type and NNRTI-resistant HIV-1. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 54:718-727. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Chemical Information

