Novel mechanism of glycopeptide resistance in the A40926 producer Nonomuraea sp. ATCC 39727
- PMID: 20308385
- PMCID: PMC2876364
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.00106-10
Novel mechanism of glycopeptide resistance in the A40926 producer Nonomuraea sp. ATCC 39727
Abstract
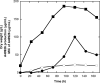
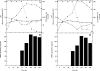
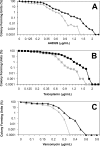
In glycopeptide-resistant enterococci and staphylococci, high-level resistance is achieved by replacing the C-terminal d-alanyl-d-alanine of lipid II with d-alanyl-d-lactate, thus reducing glycopeptide affinity for cell wall targets. Reorganization of the cell wall in these organisms is directed by the vanHAX gene cluster. Similar self-resistance mechanisms have been reported for glycopeptide-producing actinomycetes. We investigated glycopeptide resistance in Nonomuraea sp. ATCC 39727, the producer of the glycopeptide A40926, which is the precursor of the semisynthetic antibiotic dalbavancin, which is currently in phase III clinical trials. The MIC of Nonomuraea sp. ATCC 39727 toward A40926 during vegetative growth was 4 microg/ml, but this increased to ca. 20 microg/ml during A40926 production. vanHAX gene clusters were not detected in Nonomuraea sp. ATCC 39727 by Southern hybridization or by PCR with degenerate primers. However, the dbv gene cluster for A40926 production contains a gene, vanY (ORF7), potentially encoding an enzyme capable of removing the terminal d-Ala residue of pentapeptide peptidoglycan precursors. Analysis of UDP-linked peptidoglycan precursors in Nonomuraea sp. ATCC 39727 revealed the predominant presence of the tetrapeptide UDP-MurNAc-l-Ala-d-Glu-meso-Dap-d-Ala and only traces of the pentapeptide UDP-MurNAc-l-Ala-d-Glu-meso-Dap-d-Ala-d-Ala. This suggested a novel mechanism of glycopeptide resistance in Nonomuraea sp. ATCC 39727 that was based on the d,d-carboxypeptidase activity of vanY. Consistent with this, a vanY-null mutant of Nonomuraea sp. ATCC 39727 demonstrated a reduced level of glycopeptide resistance, without affecting A40926 productivity. Heterologous expression of vanY in a sensitive Streptomyces species, Streptomyces venezuelae, resulted in higher levels of glycopeptide resistance.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Relationship between glycopeptide production and resistance in the actinomycete Nonomuraea sp. ATCC 39727.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2014 Sep;58(9):5191-201. doi: 10.1128/AAC.02626-14. Epub 2014 Jun 23. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2014. PMID: 24957828 Free PMC article.
-
Streptomyces spp. as efficient expression system for a D,D-peptidase/D,D-carboxypeptidase involved in glycopeptide antibiotic resistance.BMC Biotechnol. 2013 Mar 16;13:24. doi: 10.1186/1472-6750-13-24. BMC Biotechnol. 2013. PMID: 23497129 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of VanYn, a novel D,D-peptidase/D,D-carboxypeptidase involved in glycopeptide antibiotic resistance in Nonomuraea sp. ATCC 39727.FEBS J. 2012 Sep;279(17):3203-13. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2012.08706.x. Epub 2012 Aug 2. FEBS J. 2012. PMID: 22788848
-
Understanding and manipulating glycopeptide pathways: the example of the dalbavancin precursor A40926.J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol. 2006 Jul;33(7):569-76. doi: 10.1007/s10295-006-0124-1. Epub 2006 Apr 26. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol. 2006. PMID: 16761167 Review.
-
Old and New Glycopeptide Antibiotics: Action and Resistance.Antibiotics (Basel). 2014 Nov 4;3(4):572-94. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics3040572. Antibiotics (Basel). 2014. PMID: 27025757 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Genomic-Led Discovery of a Novel Glycopeptide Antibiotic by Nonomuraea coxensis DSM 45129.ACS Chem Biol. 2021 May 21;16(5):915-928. doi: 10.1021/acschembio.1c00170. Epub 2021 Apr 29. ACS Chem Biol. 2021. PMID: 33913701 Free PMC article.
-
Occurrence of vanHAX and Related Genes beyond the Actinobacteria Phylum.Genes (Basel). 2022 Oct 27;13(11):1960. doi: 10.3390/genes13111960. Genes (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36360197 Free PMC article.
-
Specificity of Induction of Glycopeptide Antibiotic Resistance in the Producing Actinomycetes.Antibiotics (Basel). 2018 Apr 25;7(2):36. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics7020036. Antibiotics (Basel). 2018. PMID: 29693566 Free PMC article.
-
Complex Regulatory Networks Governing Production of the Glycopeptide A40926.Antibiotics (Basel). 2018 Apr 5;7(2):30. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics7020030. Antibiotics (Basel). 2018. PMID: 29621136 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Glycopeptide Antibiotic Resistance Genes: Distribution and Function in the Producer Actinomycetes.Front Microbiol. 2020 Jun 17;11:1173. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.01173. eCollection 2020. Front Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32655512 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Arthur, M., F. Depardieu, L. Cabanie, P. Reynolds, and P. Courvalin. 1998. Requirement of the VanY and VanX d,d-peptidases for glycopeptide resistance in enterococci. Mol. Microbiol. 30:819-830. - PubMed
-
- Beltrametti, F., A. Lazzarini, C. Brunati, E. Selva, and F. Marinelli. 2003. Production of demannosyl-A40926 by a Nonomuraea sp. ATCC 39727 mutant strain. J. Antibiot. (Tokyo) 56:310-313. - PubMed
-
- Beltrametti, F., A. Consolandi, L. Carrano, F. Bagatin, R. Rossi, L. Leoni, E. Zennaro, E. Selva, and F. Marinelli. 2007. Resistance to glycopeptide antibiotics in the teicoplanin producer is mediated by van gene homologue expression directing the synthesis of a modified cell wall peptidoglycan. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 51:1135-1141. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Beltrametti, F., S. Jovetic, M. Feroggio, L. Gastaldo, E. Selva, and F. Marinelli. 2004. Valine influences production and complex composition of glycopeptide antibiotic A40926 in fermentations of Nonomuraea sp. ATCC 39727. J. Antibiot. (Tokyo). 57:37-44. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

