A genome-scale protein interaction profile of Drosophila p53 uncovers additional nodes of the human p53 network
- PMID: 20308539
- PMCID: PMC2851947
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1002447107
A genome-scale protein interaction profile of Drosophila p53 uncovers additional nodes of the human p53 network
Abstract
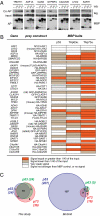
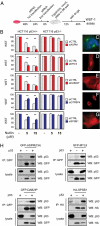
The genome of the fruitfly Drosophila melanogaster contains a single p53-like protein, phylogenetically related to the ancestor of the mammalian p53 family of tumor suppressors. We reasoned that a comprehensive map of the protein interaction profile of Drosophila p53 (Dmp53) might help identify conserved interactions of the entire p53 family in man. Using a genome-scale in vitro expression cloning approach, we identified 91 previously unreported Dmp53 interactors, considerably expanding the current Drosophila p53 interactome. Looking for evolutionary conservation of these interactions, we tested 41 mammalian orthologs and found that 37 bound to one or more p53-family members when overexpressed in human cells. An RNAi-based functional assay for modulation of the p53 pathway returned five positive hits, validating the biological relevance of these interactions. One p53 interactor is GTPBP4, a nucleolar protein involved in 60S ribosome biogenesis. We demonstrate that GTPBP4 knockdown induces p53 accumulation and activation in the absence of nucleolar disruption. In breast tumors with wild-type p53, increased expression of GTPBP4 correlates with reduced patient survival, emphasizing a potential relevance of this regulatory axis in cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

