Inducible gene expression from the plastid genome by a synthetic riboswitch
- PMID: 20308585
- PMCID: PMC2852001
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0914423107
Inducible gene expression from the plastid genome by a synthetic riboswitch
Abstract
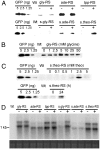
Riboswitches are natural RNA sensors that regulate gene expression in response to ligand binding. Riboswitches have been identified in prokaryotes and eukaryotes but are unknown in organelles (mitochondria and plastids). Here we have tested the possibility to engineer riboswitches for plastids (chloroplasts), a genetic system that largely relies on translational control of gene expression. To this end, we have used bacterial riboswitches and modified them in silico to meet the requirements of translational regulation in plastids. These engineered switches were then tested for functionality in vivo by stable transformation of the tobacco chloroplast genome. We report the identification of a synthetic riboswitch that functions as an efficient translational regulator of gene expression in plastids in response to its exogenously applied ligand theophylline. This riboswitch provides a novel tool for plastid genome engineering that facilitates the tightly regulated inducible expression of chloroplast genes and transgenes and thus has wide applications in functional genomics and biotechnology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Boosting riboswitch efficiency by RNA amplification.Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 May 26;43(10):e66. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv165. Epub 2015 Mar 30. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015. PMID: 25824954 Free PMC article.
-
Systematic Comparison and Rational Design of Theophylline Riboswitches for Effective Gene Repression.Microbiol Spectr. 2023 Feb 14;11(1):e0275222. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.02752-22. Epub 2023 Jan 23. Microbiol Spectr. 2023. PMID: 36688639 Free PMC article.
-
Design criteria for synthetic riboswitches acting on transcription.RNA Biol. 2015;12(2):221-31. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2015.1017235. RNA Biol. 2015. PMID: 25826571 Free PMC article.
-
Engineering and In Vivo Applications of Riboswitches.Annu Rev Biochem. 2017 Jun 20;86:515-539. doi: 10.1146/annurev-biochem-060815-014628. Epub 2017 Mar 30. Annu Rev Biochem. 2017. PMID: 28375743 Review.
-
Transgenic plastids in basic research and plant biotechnology.J Mol Biol. 2001 Sep 21;312(3):425-38. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.2001.4960. J Mol Biol. 2001. PMID: 11563907 Review.
Cited by
-
Transgene insertion into the plastid genome alters expression of adjacent native chloroplast genes at the transcriptional and translational levels.Plant Biotechnol J. 2023 Apr;21(4):711-725. doi: 10.1111/pbi.13985. Epub 2023 Jan 17. Plant Biotechnol J. 2023. PMID: 36529916 Free PMC article.
-
Plant plastid engineering.Curr Genomics. 2010 Nov;11(7):500-12. doi: 10.2174/138920210793175912. Curr Genomics. 2010. PMID: 21532834 Free PMC article.
-
Synthetic RNA switches as a tool for temporal and spatial control over gene expression.Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2012 Oct;23(5):679-88. doi: 10.1016/j.copbio.2012.01.005. Epub 2012 Feb 3. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2012. PMID: 22305712 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RNA elements and their biotechnological applications in plants.New Phytol. 2025 Sep;247(6):2517-2537. doi: 10.1111/nph.70400. Epub 2025 Jul 27. New Phytol. 2025. PMID: 40717389 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mining Functional Elements in Messenger RNAs: Overview, Challenges, and Perspectives.Front Plant Sci. 2011 Nov 30;2:84. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2011.00084. eCollection 2011. Front Plant Sci. 2011. PMID: 22639614 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

