Organizing the cell cortex: the role of ERM proteins
- PMID: 20308985
- PMCID: PMC2871950
- DOI: 10.1038/nrm2866
Organizing the cell cortex: the role of ERM proteins
Erratum in
- Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2010 Sep;11(9):674
Abstract
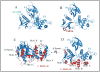
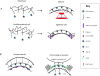
Specialized membrane domains are an important feature of almost all cells. In particular, they are essential to tissues that have a highly organized cell cortex, such as the intestinal brush border epithelium. The ERM proteins (ezrin, radixin and moesin) have a crucial role in organizing membrane domains through their ability to interact with transmembrane proteins and the cytoskeleton. In doing so, they can provide structural links to strengthen the cell cortex and regulate the activities of signal transduction pathways. Recent studies examining the structure and in vivo functions of ERMs have greatly advanced our understanding of the importance of membrane-cytoskeleton interactions.
Figures



References
-
- Saotome I, Curto M, McClatchey AI. Ezrin is essential for epithelial organization and villus morphogenesis in the developing intestine. Dev Cell. 2004;6:855–64. This work provides a detailed phenotypic analysis of epithelial defects in the intestine of mice defficient for ezrin, demonstrating that ezrin plays a crucial role in lumen morphogenesis in the gut. - PubMed
-
- Kunda P, Pelling AE, Liu T, Baum B. Moesin controls cortical rigidity, cell rounding, and spindle morphogenesis during mitosis. Curr Biol. 2008;18:91–101. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

