The final steps of integrin activation: the end game
- PMID: 20308986
- PMCID: PMC3929966
- DOI: 10.1038/nrm2871
The final steps of integrin activation: the end game
Abstract
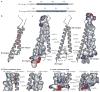
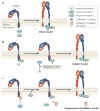
Cell-directed changes in the ligand-binding affinity ('activation') of integrins regulate cell adhesion and migration, extracellular matrix assembly and mechanotransduction, thereby contributing to embryonic development and diseases such as atherothrombosis and cancer. Integrin activation comprises triggering events, intermediate signalling events and, finally, the interaction of integrins with cytoplasmic regulators, which changes an integrin's affinity for its ligands. The first two events involve diverse interacting signalling pathways, whereas the final steps are immediately proximal to integrins, thus enabling integrin-focused therapeutic strategies. Recent progress provides insight into the structure of integrin transmembrane domains, and reveals how the final steps of integrin activation are mediated by integrin-binding proteins such as talins and kindlins.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
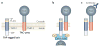
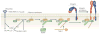
References
-
- Hynes RO. Integrins: bidirectional, allosteric signaling machines. Cell. 2002;110:673–687. - PubMed
-
- Ginsberg MH, Partridge A, Shattil SJ. Integrin regulation. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2005;17:509–516. - PubMed
-
- Petrich BG, et al. The antithrombotic potential of selective blockade of talin-dependent integrin αIIbβ3 (platelet GPIIb-IIIa) activation. J Clin Invest. 2007;117:2250–2259. Shows that the mutational inhibition of talin 1 binding to the β3 integrin tail prevents activation of αIIbβ3 integrin, resulting in protection from thrombosis without spontaneous pathological bleeding. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Carman CV, Springer TA. Integrin avidity regulation: are changes in affinity and conformation underemphasized? Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2003;15:547–556. - PubMed
-
- Bazzoni G, Hemler ME. Are changes in integrin affinity and conformation overemphasized? Trends Biochem Sci. 1998;23:30–34. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

