Environmental enrichment requires adult neurogenesis to facilitate the recovery from psychosocial stress
- PMID: 20308988
- PMCID: PMC2990187
- DOI: 10.1038/mp.2010.34
Environmental enrichment requires adult neurogenesis to facilitate the recovery from psychosocial stress
Abstract
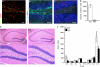
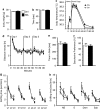
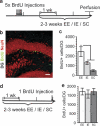
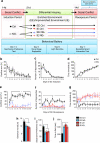
The subgranular zone of the adult hippocampal dentate gyrus contains a pool of neural stem cells that continuously divide and differentiate into functional granule cells. It has been shown that production of new hippocampal neurons is necessary for amelioration of stress-induced behavioral changes by antidepressants in animal models of depression. The survival of newly born hippocampal neurons is decreased by chronic psychosocial stress and increased by exposure to enriched environments. These observations suggest the existence of a link between hippocampal neurogenesis, stress-induced behavioral changes, and the beneficial effects of enriched environment. To show causality, we subjected transgenic mice with conditionally suppressed neurogenesis to psychosocial stress followed by environmental enrichment. First, we showed that repeated social defeat coupled with chronic exposure to an aggressor produces robust and quantifiable indices of submissive and depressive-like behaviors; second, subsequent exposure to an enriched environment led to extinction of the submissive phenotype, while animals exposed to an impoverished environment retained the submissive phenotype; and third, enrichment was not effective in reversing the submissive and depressive-like behaviors in transgenic mice lacking neurogenesis. Our data show two main findings. First, living in an enriched environment is highly effective in extinguishing submissive behavioral traits developed during chronic social stress, and second, these effects are critically dependent on adult neurogenesis, indicating that beneficial behavioral adaptations are dependent on intact adult neurogenesis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Glucocorticoids orchestrate divergent effects on mood through adult neurogenesis.J Neurosci. 2013 Feb 13;33(7):2961-72. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3878-12.2013. J Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23407954 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic Social Stress Affects Synaptic Maturation of Newly Generated Neurons in the Adult Mouse Dentate Gyrus.Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2015 Sep 7;19(3):pyv097. doi: 10.1093/ijnp/pyv097. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2015. PMID: 26346341 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of local inhibitory circuits in the dentate gyrus by adult-born neurons.Hippocampus. 2016 Jun;26(6):763-78. doi: 10.1002/hipo.22557. Epub 2016 Feb 8. Hippocampus. 2016. PMID: 26662922 Free PMC article.
-
Adult neurogenesis and the plasticity of the dentate gyrus network.Eur J Neurosci. 2011 Mar;33(6):1055-61. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2011.07603.x. Eur J Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 21395848 Review.
-
Steps towards standardized quantification of adult neurogenesis.Nat Commun. 2020 Aug 26;11(1):4275. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-18046-y. Nat Commun. 2020. PMID: 32848155 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis Regulation of Adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis.Brain Plast. 2022 Oct 21;8(1):97-119. doi: 10.3233/BPL-220141. eCollection 2022. Brain Plast. 2022. PMID: 36448039 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Environmental enrichment and gut inflammation modify stress-induced c-Fos expression in the mouse corticolimbic system.PLoS One. 2013;8(1):e54811. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0054811. Epub 2013 Jan 17. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23349972 Free PMC article.
-
A sensitive period for GABAergic interneurons in the dentate gyrus in modulating sensorimotor gating.J Neurosci. 2013 Apr 10;33(15):6691-704. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0032-12.2013. J Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23575865 Free PMC article.
-
Differential paraventricular nucleus activation and behavioral responses to social isolation in prairie voles following environmental enrichment with and without physical exercise.Soc Neurosci. 2021 Aug;16(4):375-390. doi: 10.1080/17470919.2021.1926320. Epub 2021 May 24. Soc Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 33947321 Free PMC article.
-
The Mitochondrial Antioxidant Sirtuin3 Cooperates with Lipid Metabolism to Safeguard Neurogenesis in Aging and Depression.Cells. 2021 Dec 29;11(1):90. doi: 10.3390/cells11010090. Cells. 2021. PMID: 35011652 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nithianantharajah J, Hannan AJ. Enriched environments, experience-dependent plasticity and disorders of the nervous system. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2006;7:697–709. - PubMed
-
- Fox C, Merali Z, Harrison C. Therapeutic and protective effect of environmental enrichment against psychogenic and neurogenic stress. Behavioural Brain Res. 2006;175:1–8. - PubMed
-
- Caspi A, Sugden K, Moffitt TE, Taylor A, Craig IW, Harrington H, et al. Influence of life stress on depression: moderation by a polymorphism in the 5-HTT gene. Science. 2003;301:386–389. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

