Effect of cold ischemia time on the early outcome of human hepatic allografts preserved with UW solution
- PMID: 2031256
- PMCID: PMC2965604
- DOI: 10.1097/00007890-199105000-00013
Effect of cold ischemia time on the early outcome of human hepatic allografts preserved with UW solution
Abstract
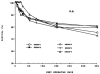
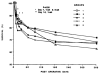
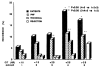
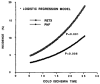
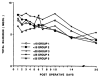
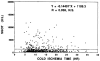
Five hundred ninety-three cadaveric livers were used for primary liver transplantation between October 24, 1987, and May 19, 1989. The grafts were procured with a combined method, using in situ cooling with cold electrolyte solution and backtable flushing with UW solution. The mean cold-ischemia time was 12.8 (range 2.4-34.7) hr. The cases were divided into 5 groups according to the cold-ischemia time: group 1: less than 10 hr (n = 223); group 2: 10-14 hr (n = 188); group 3: 15-19 hr (n = 101); group 4: 20-24 hr (n = 52); and group 5: greater than or equal to 25 hr (n = 29). There was no difference between the 5 groups in 1-year patient survival, highest SGOT in first week after operation, and SGOT and total bilirubin during the first month after operation. However, with a logistic regression model, the retransplantation rate (P = 0.001) and primary nonfunction rate (P = 0.006) significantly rose as cold-ischemia time increased, meaning that the equivalency of patient survival was increasingly dependent on aggressive retransplantation.
Figures


References
-
- Jamieson NV, Sundberg R, Lindell S, et al. Successful 24- to 30- hour preservation of the canine liver: a preliminary report. Transplant Proc. 1988;20(Suppl 1):945.
-
- Kalayoglu M, Sollinger WH, Stratta RJ, et al. Extended preservation of the liver for clinical transplantation. Lancet. 1988;1:617. - PubMed
-
- D'Alessandro AM, Kalayoglu M, Sollinger HW, et al. Experience with Belzer UW cold storage solution in human liver transplantation. Transplant Proc. 1990;22:474. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
