Biological activity and binding site characteristics of the PA1b Entomotoxin on insects from different orders
- PMID: 20331395
- PMCID: PMC2999418
- DOI: 10.1673/031.007.1201
Biological activity and binding site characteristics of the PA1b Entomotoxin on insects from different orders
Abstract
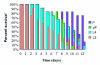
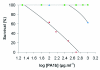
The aim of this work was to investigate both the biological activity of an entomotoxin, the pea albumin 1b (PA1b), and the presence or absence of its binding site within an array of insect species. The data obtained showed that insect sensitivity was not related to its taxonomic position. Moreover, PA1b was not toxic to several tested microorganisms. However, the binding site was found to be conserved among very different insects, displaying similar thermodynamic constants regardless of the in vivo species sensitivity. The binding site alone was, therefore, not sufficient for toxicity. One exception was the pea weevil, Bruchus pisorum, which was the only tested species without any detectable binding activity. These findings indicate that the binding site probably has an important endogenous function in insects and that adaptation to pea seeds resulted in the elimination of the toxin binding activity in two independent insect lineages. Other mechanisms are likely to interact with the toxin effects, although they are still largely unknown, but there is no evidence of any specific degradation of PA1b in the midgut of insects insensitive to the toxin, such as Drosophila melanogaster or Mamestra brassicae.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Pea Albumin 1 subunit b (PA1b), a promising bioinsecticide of plant origin.Toxins (Basel). 2011 Dec;3(12):1502-17. doi: 10.3390/toxins3121502. Epub 2011 Dec 8. Toxins (Basel). 2011. PMID: 22295174 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PA1b, an insecticidal protein extracted from pea seeds (Pisum sativum): 1H-2-D NMR study and molecular modeling.Biochemistry. 2003 Oct 21;42(41):11915-23. doi: 10.1021/bi034803l. Biochemistry. 2003. PMID: 14556622
-
Characterization of a high-affinity binding site for the pea albumin 1b entomotoxin in the weevil Sitophilus.Eur J Biochem. 2003 Jun;270(11):2429-35. doi: 10.1046/j.1432-1033.2003.03611.x. Eur J Biochem. 2003. PMID: 12755698
-
Host range of the potential biopesticide Pea Albumin 1b (PA1b) is limited to insects.Toxicon. 2014 Oct;89:67-76. doi: 10.1016/j.toxicon.2014.07.004. Epub 2014 Jul 23. Toxicon. 2014. PMID: 25064271
-
[Advances in receptor-mediated resistance mechanisms of Lepidopteran insects to Bacillus thuringiensis toxin].Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao. 2022 May 25;38(5):1809-1823. doi: 10.13345/j.cjb.210834. Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao. 2022. PMID: 35611730 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Vicia sativa subsp. sativa native to the Middle East comprises Pea Albumin1 b-like homologs: A promising natural biopesticide.Heliyon. 2024 Feb 24;10(5):e26903. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e26903. eCollection 2024 Mar 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38439846 Free PMC article.
-
Pea Albumin 1 subunit b (PA1b), a promising bioinsecticide of plant origin.Toxins (Basel). 2011 Dec;3(12):1502-17. doi: 10.3390/toxins3121502. Epub 2011 Dec 8. Toxins (Basel). 2011. PMID: 22295174 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fine Mapping and Characterization of an Aphid-Resistance Gene in the Soybean Landrace Fangzheng Moshidou.Front Plant Sci. 2022 Jun 15;13:899212. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.899212. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 35783980 Free PMC article.
-
The interaction of the bioinsecticide PA1b (Pea Albumin 1 subunit b) with the insect V-ATPase triggers apoptosis.Sci Rep. 2017 Jul 7;7(1):4902. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-05315-y. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28687751 Free PMC article.
-
Toxins for transgenic resistance to hemipteran pests.Toxins (Basel). 2012 Jun;4(6):405-29. doi: 10.3390/toxins4060405. Epub 2012 Jun 4. Toxins (Basel). 2012. PMID: 22822455 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Azzouz H, Cherqui A, Campan EDM, Rahbé Y, Duport G, Jouanin L, Kaiser L, Giordanengo P. Effects of plant protease inhibitors, oryzacystatin I and soybean Bowman-Birk inhibitor, on the aphid Macrosiphum euphorbiae(Homoptera, Aphididae) and its parasitoid Aphelinus abdominalis (Hymenoptera, Aphelinidae). Journal of Insect Physiology. 2005;51:75–86. - PubMed
-
- Craik DJ, Daly NL, Waine C. The cystine knot motif in toxins and implications for drug design. Toxicon. 2001;39:43–60. - PubMed
-
- Delobel B, Grenier A, Gueguen J, Ferrasson E, Mbailao M. Utilistion d'un polypeptide dérivé d'une albumine PA1b de légumineuse comme insecticide. French Patent # 98 05877; 1998.
-
- Deraison C, Darboux I, Duportets L, Dorojankina T, Rahbé Y, Jouanin L. Cloning and characterization of a gut-specific cathepsin L from the aphid Aphis gossypii. Insect molecular biology. 2004;13:165–177. - PubMed
-
- Gatehouse AMR, Gatehouse JA. Identifying proteins with insecticidal activity: use of encoding genes to produce insect-resistant transgenic crops. Pesticide Science. 1998;52:165–175.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

