Effects of acupuncture to treat fibromyalgia: a preliminary randomised controlled trial
- PMID: 20331844
- PMCID: PMC2852376
- DOI: 10.1186/1749-8546-5-11
Effects of acupuncture to treat fibromyalgia: a preliminary randomised controlled trial
Abstract
Background: Acupuncture is often used to treat fibromyalgia (FM), but it remains unclear whether acupuncture is effective. This study aims to evaluate the effects of acupuncture on pain and quality of life (QoL) in FM patients.
Methods: Sixteen patients (13 women and 3 men aged 25-63 years) suffering from FM were randomised into two groups: group A (n = 8) received five acupuncture treatments after the fifth week and group B received ten acupuncture treatments. Outcome measures used in this study were pain intensity (visual analogue scale, VAS) and the fibromyalgia impact questionnaire (FIQ).
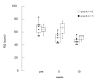
Results: After the fifth week, pain intensity (U = 25.0; P = 0.022) in group B decreased and QoL (U = 24.5; P = 0.026) improved compared to group A.
Conclusion: The present study suggests that acupuncture treatment is effective to relieve pain for FM patients in terms of QoL and FIQ.
Figures


References
-
- Wolfe F, Smythe HA, Yunus MB, Bennett RM, Bombardier C, Goldenberg DL, Tugwell P, Campbell SM, Abeles M, Clark P, Fam AG, Farber SJ, Fiectner JJ, Franklin CM, Gatter RA, Hamaty D, Lessard J, Lichtbroun AS, Masi AT, Mccain GA, Reynolds J, Romano TJ, Russell IJ, Sheon RP. The American College of Rheumatology 1990 crireria for the classification of fibromyalgia. Report of the multicenter criteria committee. Arthritis Rheum. 1990;33:160–172. doi: 10.1002/art.1780330203. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

