Near-infrared spectroscopy during stagnant ischemia estimates central venous oxygen saturation and mixed venous oxygen saturation discrepancy in patients with severe left heart failure and additional sepsis/septic shock
- PMID: 20331856
- PMCID: PMC2887154
- DOI: 10.1186/cc8929
Near-infrared spectroscopy during stagnant ischemia estimates central venous oxygen saturation and mixed venous oxygen saturation discrepancy in patients with severe left heart failure and additional sepsis/septic shock
Abstract
Introduction: Discrepancies of 5-24% between superior vena cava oxygen saturation (ScvO2) and mixed venous oxygen saturation (SvO2) have been reported in patients with severe heart failure. Thenar muscle tissue oxygenation (StO2) measured with near-infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) during arterial occlusion testing decreases slower in sepsis/septic shock patients (lower StO2 deoxygenation rate). The StO2 deoxygenation rate is influenced by dobutamine. The aim of this study was to determine the relationship between the StO2 deoxygenation rate and the ScvO2-SvO2 discrepancy in patients with severe left heart failure and additional sepsis/septic shock treated with or without dobutamine.
Methods: Fifty-two patients with severe left heart failure due to primary heart disease with additional severe sepsis/septic shock were included. SvO2 and ScvO2 were compared to the thenar muscle StO2 before and during arterial occlusion.
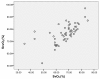
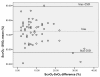
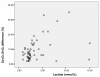
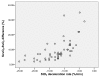
Results: SvO2 correlated significantly with ScvO2 (Pearson correlation 0.659, P = 0.001), however, Bland Altman analysis showed a clinically important difference between both variables (ScvO2-SvO2 mean 72 +/- 8%, ScvO2-SvO2 difference 9.4 +/- 7.5%). The ScvO2-SvO2 difference correlated with plasma lactate (Pearson correlation 0.400, P = 0.003) and the StO2 deoxygenation rate (Pearson correlation 0.651, P = 0.001). In the group of patients treated with dobutamine, the ScvO2-SvO2 difference correlated with plasma lactate (Pearson correlation 0.389, P = 0.011) and the StO2 deoxygenation rate (Pearson correlation 0.777, P = 0.0001).
Conclusions: In patients with severe heart failure with additional severe sepsis/septic shock the ScvO2-SvO2 discrepancy presents a clinical problem. In these patients the skeletal muscle StO2 deoxygenation rate is inversely proportional to the difference between ScvO2 and SvO2; dobutamine does not influence this relationship. When using ScvO2 as a treatment goal, the NIRS measurement may prove to be a useful non-invasive diagnostic test to uncover patients with a normal ScvO2 but potentially an abnormally low SvO2.
Trial registration: NCT00384644 ClinicalTrials.Gov.
Figures
Comment in
-
Tissue saturation measurement--exciting prospects, but standardisation and reference data still needed.Crit Care. 2010;14(3):169. doi: 10.1186/cc8970. Epub 2010 Jun 24. Crit Care. 2010. PMID: 20619003 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barratt-Boyes Bg, Wood EH. The oxygen saturation of blood in vena cava, right heart chambers and pulmonary vessels of healthy subjects. J Lab Clin Med. 1957;50:93–106. - PubMed
-
- Scheinman MM, Brown MA, Rapaport E. Critical assesment of use of central venous oxygen saturation as a mirror of mixed venous oxygen saturation in severly ill cardiac patients. Circulation. 1969;40:165–172. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

