FDA approval summary: temsirolimus as treatment for advanced renal cell carcinoma
- PMID: 20332142
- PMCID: PMC3227966
- DOI: 10.1634/theoncologist.2009-0178
FDA approval summary: temsirolimus as treatment for advanced renal cell carcinoma
Abstract
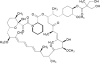
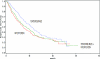
This report summarizes the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA)'s approval of temsirolimus (Torisel), on May 30, 2007, for the treatment of advanced renal cell carcinoma (RCC). Information provided includes regulatory history, study design, study results, and literature review. A multicenter, three-arm, randomized, open-label study was conducted in previously untreated patients with poor-prognosis, advanced RCC. The study objectives were to compare overall survival (OS), progression-free survival (PFS), objective response rate, and safety in patients receiving interferon (IFN)-alpha versus those receiving temsirolimus alone or in combination with IFN-alpha. In the second planned interim analysis of the intent-to-treat population (n = 626), there was a statistically significant longer OS time in the temsirolimus (25 mg) arm than in the IFN-alpha arm (median, 10.9 months versus 7.3 months; hazard ratio [HR], 0.73; p = .0078). The combination of temsirolimus (15 mg) and IFN-alpha did not lead to a significant difference in OS compared with IFN-alpha alone. There was also a statistically significant longer PFS time for the temsirolimus (25 mg) arm than for the IFN-alpha arm (median, 5.5 months versus 3.1 months; HR, 0.66, p = .0001). Common adverse reactions reported in patients receiving temsirolimus were rash, asthenia, and mucositis. Common laboratory abnormalities were anemia, hyperglycemia, hyperlipidemia, and hypertriglyceridemia. Serious but rare cases of interstitial lung disease, bowel perforation, and acute renal failure were observed. Temsirolimus has demonstrated superiority in terms of OS and PFS over IFN-alpha and provides an additional treatment option for patients with advanced RCC.
Conflict of interest statement
Section editor
The content of this article has been reviewed by independent peer reviewers to ensure that it is balanced, objective, and free from commercial bias.
Figures
Comment in
-
Temsirolimus: is improved survival the correct expression of drug activity?Oncologist. 2010;15(7):790-1; author reply 792. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2010-0099. Oncologist. 2010. PMID: 20667970 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Madison, NJ: Wyeth Pharmaceuticals, Inc.; Rapamune® [product label]
-
- American Cancer Society, Inc., Surveillance and Health Policy Research. Estimated new cancer cases and deaths by sex, US, 2009. [accessed March 11, 2010]. Available at http://www.cancer.org/docroot/MED/content/downloads/MED_1_1x_CFF2009_Est....
-
- Couillard DR, DeVere White RW. Surgery of RCC. Urol Clin North Am. 1993;20:263–275. - PubMed
-
- DeVita VT, Jr, Lawrence TS, Rosenberg SA. Cancer Principles and Practice of Oncology. Eight Edition. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2008. pp. 1–2938.
-
- Kane RC, Farrell AT, Saber H, et al. Sorafenib for the treatment of advanced renal cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2006;12:7271–7278. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous