Golgi-modifying properties of macfarlandin E and the synthesis and evaluation of its 2,7-dioxabicyclo[3.2.1]octan-3-one core
- PMID: 20332207
- PMCID: PMC2851978
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1001421107
Golgi-modifying properties of macfarlandin E and the synthesis and evaluation of its 2,7-dioxabicyclo[3.2.1]octan-3-one core
Abstract
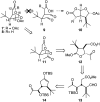
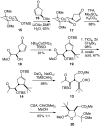
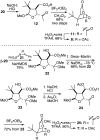
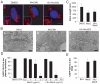
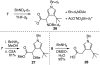
Golgi-modifying properties of the spongian diterpene macfarlandin E (MacE) and a synthetic analog, t-Bu-MacE, containing its 2,7-dioxabicyclo[3.2.1]octan-3-one moiety are reported. Natural product screening efforts identified MacE as inducing a novel morphological change in Golgi structure defined by ribbon fragmentation with maintenance of the resulting Golgi fragments in the pericentriolar region. t-Bu-MacE, which possesses the substituted 2,7-dioxabicyclo[3.2.1]octan-3-one but contains a tert-butyl group in place of the hydroazulene subunit of MacE, was prepared by chemical synthesis. Examination of the Golgi-modifying properties of MacE, t-Bu-MacE, and several related structures revealed that the entire oxygen-rich bridged-bicyclic fragment is required for induction of this unique Golgi organization phenotype. Further characterization of MacE-induced Golgi modification showed that protein secretion is inhibited, with no effect on the actin or microtubule cytoskeleton being observed. The conversion of t-Bu-MacE and a structurally related des-acetoxy congener to substituted pyrroles in the presence of primary amines in protic solvent at ambient temperatures suggests that covalent modification might be involved in the Golgi-altering activity of MacE.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
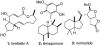
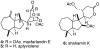

References
-
- Donaldson JG, Finazzi D, Klausner RD. Brefeldin A inhibits Golgi membrane-catalysed exchange of guanine nucleotide onto ARF protein. Nature. 1992;360:350–352. - PubMed
-
- Renault L, Guibert B, Cherfils J. Structural snapshots of the mechanism and inhibition of a guanine nucleotide exchange factor. Nature. 2003;426:525–530. - PubMed
-
- Takizawa PA, et al. Complete vesiculation of Golgi membranes and inhibition of protein-transport by a novel sea sponge metabolite, ilimaquinone. Cell. 1993;73:1079–1090. - PubMed
-
- Radeke HS, Digits CA, Casaubon RL, Snapper ML. Interactions of (-)-ilimaquinone with methylation enzymes: Implications for vesicular-mediated secretion. Chem Biol. 1999;6:639–647. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

