PTPH1 dephosphorylates and cooperates with p38gamma MAPK to increase ras oncogenesis through PDZ-mediated interaction
- PMID: 20332238
- PMCID: PMC2848905
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-3229
PTPH1 dephosphorylates and cooperates with p38gamma MAPK to increase ras oncogenesis through PDZ-mediated interaction
Abstract
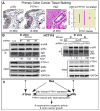
Protein phosphatases are believed to coordinate with kinases to execute biological functions, but examples of such integrated activities, however, are still missing. In this report, we have identified protein tyrosine phosphatase H1 (PTPH1) as a specific phosphatase for p38gamma mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) and shown their cooperative oncogenic activity through direct binding. p38gamma, a Ras effector known to act independent of its phosphorylation, was first shown to require its unique PDZ-binding motif to increase Ras transformation. Yeast two-hybrid screening and in vitro and in vivo analyses further identified PTPH1 as a specific p38gamma phosphatase through PDZ-mediated binding. Additional experiments showed that PTPH1 itself plays a role in Ras-dependent malignant growth in vitro and/or in mice by a mechanism depending on its p38gamma-binding activity. Moreover, Ras increases both p38gamma and PTPH1 protein expression and there is a coupling of increased p38gamma and PTPH1 protein expression in primary colon cancer tissues. These results reveal a coordinative oncogenic activity of a MAPK with its specific phosphatase and suggest that PDZ-mediated p38gamma/PTPH1 complex may be a novel target for Ras-dependent malignancies.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflicts of interest were disclosed.
Figures





References
-
- Downward J. Targeting Ras signalling pathways in cancer therapy. Nature Rev Cancer. 2003;3:11–22. - PubMed
-
- Han J, Sun P. The pathways to tumor supression via route p38. Trends Biochem Sci. 2007;32:364–71. - PubMed
-
- Chen G, Hitomi M, Han J, Stacey DW. The p38 pathway provides negative feedback to Ras proliferative signaling. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:38973–80. - PubMed
-
- Qi X, Tang J, Pramanik R, et al. p38 MAPK activation selectively induces cell death in K-ras mutated human colon cancer cells through regulation of vitamin D receptor. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:22138–44. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

