Effects of exenatide and lifestyle modification on body weight and glucose tolerance in obese subjects with and without pre-diabetes
- PMID: 20332357
- PMCID: PMC2875418
- DOI: 10.2337/dc09-1203
Effects of exenatide and lifestyle modification on body weight and glucose tolerance in obese subjects with and without pre-diabetes
Abstract
Objective: To assess the effects of exenatide on body weight and glucose tolerance in nondiabetic obese subjects with normal or impaired glucose tolerance (IGT) or impaired fasting glucose (IFG).
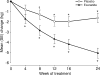
Research design and methods: Obese subjects (n = 152; age 46 +/- 12 years, female 82%, weight 108.6 +/- 23.0 kg, BMI 39.6 +/- 7.0 kg/m(2), IGT or IFG 25%) were randomized to receive exenatide (n = 73) or placebo (n = 79), along with lifestyle intervention, for 24 weeks. RESULTS Exenatide-treated subjects lost 5.1 +/- 0.5 kg from baseline versus 1.6 +/- 0.5 kg with placebo (exenatide--placebo, P < 0.001). Placebo-subtracted difference in percent weight reduction was -3.3 +/- 0.5% (P < 0.001). Both groups reduced their daily calorie intake (exenatide, -449 cal; placebo, -387 cal). IGT or IFG normalized at end point in 77 and 56% of exenatide and placebo subjects, respectively.
Conclusions: Exenatide plus lifestyle modification decreased caloric intake and resulted in weight loss in nondiabetic obesity with improved glucose tolerance in subjects with IGT and IFG.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00500370.
Figures
References
-
- Lindström J, Louheranta A, Mannelin M, Rastas M, Salminen V, Eriksson J, Uusitupa M, Tuomilehto J: Finnish Diabetes Prevention Study Group. Lifestyle intervention and 3-year results on diet and physical activity. Diabetes Care 2003;26:3230–3236 - PubMed
-
- Lindström J, Ilanne-Parikka P, Peltonen M, Aunola S, Eriksson JG, Hemiö K, Hämäläinen H, Härkönen P, Keinänen-Kiukaanniemi S, Laakso M, Louheranta A, Mannelin M, Paturi M, Sundvall J, Valle TT, Uusitupa M, Tuomilehto J: Finnish Diabetes Prevention Study Group. Sustained reduction in the incidence of type 2 diabetes by lifestyle intervention: follow-up of the Finnish Diabetes Prevention Study. Lancet 2006;368:1673–1679 - PubMed
-
- Pan XR, Li GW, Hu YH, Wang JX, Yang WY, An ZX, Hu ZX, Lin J, Xiao JZ, Cao HB, Liu PA, Jiang XG, Jiang YY, Wang JP, Zheng H, Zhang H, Bennett PH, Howard BV: Effects of diet and exercise in preventing NIDDM in people with impaired glucose tolerance. The Da Qing IGT and Diabetes Study. Diabetes Care 1997;20:537–544 - PubMed
-
- Nathan DM, Buse JB, Davidson MB, Ferrannini E, Holman RR, Sherwin R, Zinman B: American Diabetes Association, European Association for Study of Diabetes. Medical management of hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetes: a consensus algorithm for the initiation and adjustment of therapy: a consensus statement of the American Diabetes Association and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2009;32:193–203 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

