Regulation of FGF21 expression and secretion by retinoic acid receptor-related orphan receptor alpha
- PMID: 20332535
- PMCID: PMC2871432
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.102160
Regulation of FGF21 expression and secretion by retinoic acid receptor-related orphan receptor alpha
Abstract
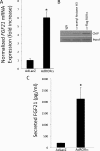
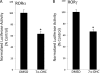
Fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21) is a hormone produced by fat and the liver that plays an important role in lipid metabolism. FGF21 expression is induced by peroxisome proliferator-actived receptor alpha in response to physiological conditions requiring increased fatty acid oxidation. Retinoic acid receptor-related receptor alpha (RORalpha) is another nuclear receptor that plays a critical role in lipid metabolism as well as in regulation of the circadian rhythm. In this study we demonstrate that RORalpha directly regulates the expression and secretion of FGF21. A canonical ROR response element was identified in the proximal promoter of the FGF21 gene and shown to exhibit functional activity. Overexpression of RORalpha in HepG2 cells resulted in increased expression and secretion of FGF21. Suppression of RORalpha expression caused a decrease in FGF21 expression and secretion, suggesting that RORalpha contributes to the basal expression of FGF21. These data suggest that one mechanism by which RORalpha regulates lipid metabolism may be by modulation of FGF21 secretion. Furthermore, this study identifies a clear link between RORalpha, a key regulator of the mammalian clock, and FGF21, an important hormone regulating glucose and lipid homeostasis.
Figures


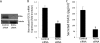
References
-
- Carlberg C., Hooft van Huijsduijnen R., Staple J. K., DeLamarter J. F., Becker-André M. (1994) Mol. Endocrinol. 8, 757–770 - PubMed
-
- Giguère V., Tini M., Flock G., Ong E., Evans R. M., Otulakowski G. (1994) Genes Dev. 8, 538–553 - PubMed
-
- Hirose T., Smith R. J., Jetten A. M. (1994) Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 205, 1976–1983 - PubMed
-
- Hamilton B. A., Frankel W. N., Kerrebrock A. W., Hawkins T. L., FitzHugh W., Kusumi K., Russell L. B., Mueller K. L., van Berkel V., Birren B. W., Kruglyak L., Lander E. S. (1996) Nature 379, 736–739 - PubMed
-
- Vu-Dac N., Gervois P., Grötzinger T., De Vos P., Schoonjans K., Fruchart J. C., Auwerx J., Mariani J., Tedgui A., Staels B. (1997) J. Biol. Chem. 272, 22401–22404 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

