Long-range bidirectional strand asymmetries originate at CpG islands in the human genome
- PMID: 20333189
- PMCID: PMC2817419
- DOI: 10.1093/gbe/evp024
Long-range bidirectional strand asymmetries originate at CpG islands in the human genome
Abstract
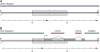
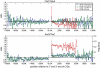
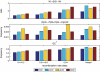
In the human genome, CpG islands (CGIs), which are GC- and CpG-rich sequences, are associated with transcription starting sites (TSSs); in addition, there is evidence that CGIs harbor origins of bidirectional replication (OBRs) and are preferred sites for heteroduplex formation during recombination. Transcription, replication, and recombination processes are known to induce specific mutational patterns in various genomes, and therefore, these patterns are expected to be found around CGIs. We use triple alignments of human, chimp, and macaque to compute the rates of nucleotide substitutions in up to 1 Mbps long intergenic regions on both sides of CGIs. Our analysis revealed that around a CGI there is an asymmetry between complementary substitution rates that is similar to the one that found around the OBR in bacteria. We hypothesize that these asymmetries are induced by differences in the replication of the leading and lagging strand and that a significant number of CGIs overlap OBRs. Within CGIs, we observed a mutational signature of GC-biased gene conversion that is associated with recombination. We suggest that recombination has played a major role in the creation of CGIs.
Keywords: CpG islands; biased gene conversion; origin of bi-directional replication; recombination; strand asymmetries.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Germline methylation patterns determine the distribution of recombination events in the dog genome.Genome Biol Evol. 2014 Dec 19;7(2):522-30. doi: 10.1093/gbe/evu282. Genome Biol Evol. 2014. PMID: 25527838 Free PMC article.
-
Replication-associated mutational asymmetry in the human genome.Mol Biol Evol. 2011 Aug;28(8):2327-37. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msr056. Epub 2011 Mar 2. Mol Biol Evol. 2011. PMID: 21368316
-
The evolution of transcription-associated biases of mutations across vertebrates.BMC Evol Biol. 2010 Jun 18;10:187. doi: 10.1186/1471-2148-10-187. BMC Evol Biol. 2010. PMID: 20565875 Free PMC article.
-
Intragenic CpG Islands and Their Impact on Gene Regulation.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Feb 11;10:832348. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.832348. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35223855 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Decreased fidelity in replicating DNA methylation patterns in cancer cells leads to dense methylation of a CpG island.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2006;310:199-210. doi: 10.1007/3-540-31181-5_10. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2006. PMID: 16909912 Review.
Cited by
-
Linking the DNA strand asymmetry to the spatio-temporal replication program. I. About the role of the replication fork polarity in genome evolution.Eur Phys J E Soft Matter. 2012 Sep;35(9):92. doi: 10.1140/epje/i2012-12092-y. Epub 2012 Sep 26. Eur Phys J E Soft Matter. 2012. PMID: 23001787
-
Genome-wide depletion of replication initiation events in highly transcribed regions.Genome Res. 2011 Nov;21(11):1822-32. doi: 10.1101/gr.124644.111. Epub 2011 Aug 3. Genome Res. 2011. PMID: 21813623 Free PMC article.
-
Evidence for evolutionary and nonevolutionary forces shaping the distribution of human genetic variants near transcription start sites.PLoS One. 2014 Dec 4;9(12):e114432. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0114432. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25474578 Free PMC article.
-
Chimeric chromosome landscapes of human somatic cell cultures show dependence on stress and regulation of genomic repeats by CGGBP1.Oncotarget. 2022 Jan 17;13:136-155. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.28174. eCollection 2022. Oncotarget. 2022. PMID: 35070079 Free PMC article.
-
GC skew at the 5' and 3' ends of human genes links R-loop formation to epigenetic regulation and transcription termination.Genome Res. 2013 Oct;23(10):1590-600. doi: 10.1101/gr.158436.113. Epub 2013 Jul 18. Genome Res. 2013. PMID: 23868195 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aladjem MI. Replication in context: dynamic regulation of DNA replication patterns in metazoans. Nat Rev Genet. 2007;8:588–600. - PubMed
-
- Antequera F, Bird A. CpG islands as genomic footprints of promoters that are associated with replication origins. Curr Biol. 1999;9:R661–R667. - PubMed
-
- Bock C, Lengauer T. Computational epigenetics. Bioinformatics. 2008;24:1–10. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

