Advances in Nuclear Magnetic Resonance for Drug Discovery
- PMID: 20333269
- PMCID: PMC2843924
- DOI: 10.1517/17460440903232623
Advances in Nuclear Magnetic Resonance for Drug Discovery
Abstract
BACKGROUND: Drug discovery is a complex and unpredictable endeavor with a high failure rate. Current trends in the pharmaceutical industry have exasperated these challenges and are contributing to the dramatic decline in productivity observed over the last decade. The industrialization of science by forcing the drug discovery process to adhere to assembly-line protocols is imposing unnecessary restrictions, such as short project time-lines. Recent advances in nuclear magnetic resonance are responding to these self-imposed limitations and are providing opportunities to increase the success rate of drug discovery. OBJECTIVE/METHOD: A review of recent advancements in NMR technology that have the potential of significantly impacting and benefiting the drug discovery process will be presented. These include fast NMR data collection protocols and high-throughput protein structure determination, rapid protein-ligand co-structure determination, lead discovery using fragment-based NMR affinity screens, NMR metabolomics to monitor in vivo efficacy and toxicity for lead compounds, and the identification of new therapeutic targets through the functional annotation of proteins by FAST-NMR. CONCLUSION: NMR is a critical component of the drug discovery process, where the versatility of the technique enables it to continually expand and evolve its role. NMR is expected to maintain this growth over the next decade with advancements in automation, speed of structure calculation, in-cell imaging techniques, and the expansion of NMR amenable targets.
Figures


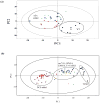
 ), wild-type with AZA (
), wild-type with AZA ( ), uaZ14 mutant with AZA (
), uaZ14 mutant with AZA ( ), and wild-type cells (◆). Results clearly demonstrate the selective activity (see Figure 7b) of AZA (Reprinted with permission from reference [201], Copyright 2006 by American Chemical Society). (b) Analysis of the in vivo activity of D-cycloserine (DCS) in mycobacteria targeting alanine racemase. PCA scores plot comparing wild-type (mc2155) (
), and wild-type cells (◆). Results clearly demonstrate the selective activity (see Figure 7b) of AZA (Reprinted with permission from reference [201], Copyright 2006 by American Chemical Society). (b) Analysis of the in vivo activity of D-cycloserine (DCS) in mycobacteria targeting alanine racemase. PCA scores plot comparing wild-type (mc2155) ( ), inactive D-alanine racemase mutant (TAM23) (●), DCS resistant mutants (GPM14 (
), inactive D-alanine racemase mutant (TAM23) (●), DCS resistant mutants (GPM14 ( ), GPM16 (
), GPM16 ( )), restored D-alanine racemase activity mutant (TAM23 pTAMU3) (
)), restored D-alanine racemase activity mutant (TAM23 pTAMU3) ( ) mc2155 with DCS (
) mc2155 with DCS ( ), and TAM23 with DCS (
), and TAM23 with DCS ( ), GPM14 with DCS (
), GPM14 with DCS ( ), GPM16 with DCS (
), GPM16 with DCS ( ), and TAM23 pTAMU3 with DCS (
), and TAM23 pTAMU3 with DCS ( ). The results clearly demonstrate the active, non-selective inhibition of DCS (see Figure 7c). The secondary target of DCS is predicted to be D-alanine-D-alanine ligase (Reprinted with permission from reference [200], Copyright 2006 by American Chemical Society).
). The results clearly demonstrate the active, non-selective inhibition of DCS (see Figure 7c). The secondary target of DCS is predicted to be D-alanine-D-alanine ligase (Reprinted with permission from reference [200], Copyright 2006 by American Chemical Society).Similar articles
-
NMR metabolomics and drug discovery.Magn Reson Chem. 2009 Dec;47 Suppl 1:S2-11. doi: 10.1002/mrc.2461. Magn Reson Chem. 2009. PMID: 19504464 Review.
-
Application of NMR and molecular docking in structure-based drug discovery.Top Curr Chem. 2012;326:1-34. doi: 10.1007/128_2011_213. Top Curr Chem. 2012. PMID: 21915777 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Translational Metabolomics of Head Injury: Exploring Dysfunctional Cerebral Metabolism with Ex Vivo NMR Spectroscopy-Based Metabolite Quantification.In: Kobeissy FH, editor. Brain Neurotrauma: Molecular, Neuropsychological, and Rehabilitation Aspects. Boca Raton (FL): CRC Press/Taylor & Francis; 2015. Chapter 25. In: Kobeissy FH, editor. Brain Neurotrauma: Molecular, Neuropsychological, and Rehabilitation Aspects. Boca Raton (FL): CRC Press/Taylor & Francis; 2015. Chapter 25. PMID: 26269925 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
Advancing fragment binders to lead-like compounds using ligand and protein-based NMR spectroscopy.Methods Enzymol. 2011;493:469-85. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-381274-2.00018-2. Methods Enzymol. 2011. PMID: 21371602
-
NMR-based screening methods for lead discovery.EXS. 2003;(93):183-202. doi: 10.1007/978-3-0348-7997-2_9. EXS. 2003. PMID: 12613177 Review.
Cited by
-
Virtual Screening Analysis and In-vitro Xanthine Oxidase Inhibitory Activity of Some Commercially Available Flavonoids.Iran J Pharm Res. 2013 Summer;12(3):317-23. Iran J Pharm Res. 2013. PMID: 24250638 Free PMC article.
-
The applicability of molecular descriptors for designing an electrospray ionization mass spectrometry compatible library for drug discovery.Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2012 Dec;15(10):806-15. doi: 10.2174/138620712803901180. Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2012. PMID: 22708878 Free PMC article.
-
In-vivo and in-silico studies revealed the molecular mechanisms of Colocasia esculenta phenolics as novel chemotherapy against benign prostatic hyperplasia via inhibition of 5α-reductase and α1-adrenoceptor.In Silico Pharmacol. 2023 Mar 1;11(1):4. doi: 10.1007/s40203-023-00141-9. eCollection 2023. In Silico Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36873908 Free PMC article.
-
NMRmix: A Tool for the Optimization of Compound Mixtures in 1D (1)H NMR Ligand Affinity Screens.J Proteome Res. 2016 Apr 1;15(4):1360-8. doi: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.6b00121. Epub 2016 Mar 23. J Proteome Res. 2016. PMID: 26965640 Free PMC article.
-
Challenges and opportunities in absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion studies of therapeutic biologics.AAPS J. 2012 Dec;14(4):781-91. doi: 10.1208/s12248-012-9388-8. Epub 2012 Aug 4. AAPS J. 2012. PMID: 22864668 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Sams-Dodd F. Target-based drug discovery: is something wrong? Drug Discovery Today. 2005;10(2):139–47. - PubMed
-
- Garnier J-P. Rebuilding the R&D engine in big pharma. Harv Bus Rev. 2008;86(5):68–70. 2–6, 128. - PubMed
-
- Weisbach JA, Moos WH. Diagnosing the decline of major pharmaceutical research laboratories: a prescription for drug companies. Drug Dev Res. 1995;34(3):243–59.
-
- Horrobin DF. Realism in drug discovery-could Cassandra be right? Nat Biotechnol. 2001;19(12):1099–100. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
