Investigating the Feasibility of 3D Dosimetry in the RPC IMRT H&N Phantom
- PMID: 20333319
- PMCID: PMC2843090
- DOI: 10.1088/1742-6596/164/1/012058
Investigating the Feasibility of 3D Dosimetry in the RPC IMRT H&N Phantom
Abstract
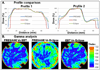
An urgent requirement for 3D dosimetry has been recognized because of high failure rate (~25%) in RPC credentialing, which relies on point and 2D dose measurements. Comprehensive 3D dosimetry is likely to resolve more errors and improve IMRT quality assurance. This work presents an investigation of the feasibility of PRESAGE/optical-CT 3D dosimetry in the Radiologic Physics Center (RPC) IMRT H&N phantom. The RPC H&N phantom (with standard and PRESAGE dosimetry inserts alternately) was irradiated with the same IMRT plan. The TLD and EBT film measurement data from standard insert irradiation was provided by RPC. The 3D dose measurement data from PRESAGE insert irradiation was readout using the OCTOPUS™ 5X optical-CT scanner at Duke. TLD, EBT and PRESAGE dose measurements were inter-compared with Eclipse calculations to evaluate consistency of planning and delivery. Results showed that the TLD point dose measurements agreed with Eclipse calculations to within 5% dose-difference. Relative dose comparison between Eclipse dose, EBT dose and PRESAGE dose was conducted using profiles and gamma comparisons (4% dose-difference and 4 mm distance-to-agreement). Profiles showed good agreement between measurement and calculation except along steep dose gradient regions where Eclipse modelling might be inaccurate. Gamma comparisons showed that the measurement and calculation showed good agreement (>96%) if edge artefacts in measurements are ignored. In conclusion, the PRESAGE/optical-CT dosimetry system was found to be feasible as an independent dosimetry tool in the RPC IMRT H&N phantom.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Investigation of the feasibility of relative 3D dosimetry in the Radiologic Physics Center Head and Neck IMRT phantom using presage/optical-CT.Med Phys. 2009 Jul;36(7):3371-7. doi: 10.1118/1.3148534. Med Phys. 2009. PMID: 19673232 Free PMC article.
-
A comprehensive evaluation of the PRESAGE/optical-CT 3D dosimetry system.Med Phys. 2009 Jan;36(1):71-82. doi: 10.1118/1.3005609. Med Phys. 2009. PMID: 19235375 Free PMC article.
-
An Investigation into the Robustness of Optical-CT Dosimetry of a Radiochromic Dosimeter Compatible with the RPC Head-and-Neck Phantom.J Phys Conf Ser. 2009 Jan 1;164(1):12059. doi: 10.1088/1742-6596/164/1/012059. J Phys Conf Ser. 2009. PMID: 20407594 Free PMC article.
-
Fast, high-resolution 3D dosimetry utilizing a novel optical-CT scanner incorporating tertiary telecentric collimation.Med Phys. 2008 Jan;35(1):101-11. doi: 10.1118/1.2804616. Med Phys. 2008. PMID: 18293567 Free PMC article.
-
SU-E-T-95: Investigation of 3D Dosimetry for an Anthropomorphic Spine Phantom.Med Phys. 2012 Jun;39(6Part11):3724. doi: 10.1118/1.4735152. Med Phys. 2012. PMID: 28517153
Cited by
-
Toward a better understanding of the gamma index: Investigation of parameters with a surface-based distance method.Med Phys. 2011 Dec;38(12):6730-41. doi: 10.1118/1.3659707. Med Phys. 2011. PMID: 22149855 Free PMC article.
-
Optical scanner for 3D radiotherapy polymer gel dosimetry.Acta Phys Pol A. 2012 Nov;122(5):969-974. doi: 10.12693/APhysPolA.122.969. Acta Phys Pol A. 2012. PMID: 30135615 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Molineu A, et al. Design and implementation of an anthropomorphic quality assurance phantom for intensity-modulated radiation therapy for the Radiation Therapy Oncology Group. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2005;63:577–583. - PubMed
-
- Radiological Physics Center Report #129. Report to the AAPM Therapy Physics Committee. 2008
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
