Early alterations in cytokine expression in adult compared to developing lung in mice after radiation exposure
- PMID: 20334525
- PMCID: PMC2859680
- DOI: 10.1667/RR1882.1
Early alterations in cytokine expression in adult compared to developing lung in mice after radiation exposure
Abstract
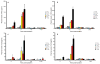
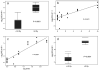
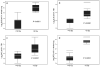
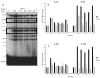
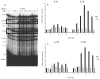
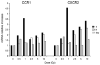
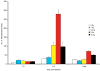
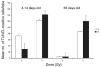
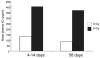
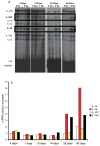
To assess early changes in the lung after low-dose radiation exposure that may serve as targets for mitigation of lung injury in the aftermath of a terrorist event, we analyzed cytokine expression after irradiation. Adult mice were studied after whole-lung or total-body irradiation. Mouse pups of different ages were also investigated after total-body irradiation. mRNA abundance was analyzed in tissue and plasma, and pathological changes were assessed. In lung tissue, dose-related changes were seen in IL1B, IL1R2 and CXCR2 mRNA expression at 1 and 6 h after irradiation, concurrent with increases in plasma protein levels of KC/CXCL1 and IL6. However, in the pups, changes in IL1 abundance were not detected until 28 days of age, coincident with the end of postnatal lung growth, although apoptosis was detected at all ages. In conclusion, although cytokines were expressed after low doses of radiation, their role in the progression of tissue response is yet to be determined. They may be candidates for use in marker-based biodosimetry. However, the lack of cytokine induction in early life suggests that different end points (and mitigating treatments) may be required for children.
Figures

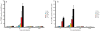
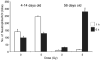
References
-
- Gonzalez AJ, Lauriston S. Taylor Lecture: Radiation protection in the aftermath of a terrorist attack involving exposure to ionizing radiation. Health Phys. 2005;89:418–446. - PubMed
-
- NIH Publication No 05-5608. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services; Washington, DC: 2005. NIH Strategic Plan and Research Agenda for Medical Countermeasures Against Radiological and Nuclear Threats.
-
- Continuation of national emergency regarding the proliferation of weapons of mass destruction. Fed Regist. 2006;71:64109.
-
- UNSCEAR. Report to the General Assembly, Annex J: Exposures and Effects of the Chernobyl Accident. United Nations; New York: 2000. Sources, Effects and Risks of Ionizing Radiation.
-
- Hirama T, Tanosaki S, Kandatsu S, Kuroiwa N, Kamada T, Tsuji H, Yamada S, Katoh H, Yamamoto N, Akashi M. Initial medical management of patients severely irradiated in the Tokai-mura criticality accident. Br J Radiol. 2003;76:246–253. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

