Differential replication of avian influenza H9N2 viruses in human alveolar epithelial A549 cells
- PMID: 20334690
- PMCID: PMC2867802
- DOI: 10.1186/1743-422X-7-71
Differential replication of avian influenza H9N2 viruses in human alveolar epithelial A549 cells
Abstract
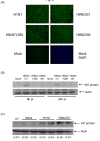
Avian influenza virus H9N2 isolates cause a mild influenza-like illness in humans. However, the pathogenesis of the H9N2 subtypes in human remains to be investigated. Using a human alveolar epithelial cell line A549 as host, we found that A/Quail/Hong Kong/G1/97 (H9N2/G1), which shares 6 viral "internal genes" with the lethal A/Hong Kong/156/97 (H5N1/97) virus, replicates efficiently whereas other H9N2 viruses, A/Duck/Hong Kong/Y280/97 (H9N2/Y280) and A/Chicken/Hong Kong/G9/97 (H9N2/G9), replicate poorly. Interestingly, we found that there is a difference in the translation of viral protein but not in the infectivity or transcription of viral genes of these H9N2 viruses in the infected cells. This difference may possibly be explained by H9N2/G1 being more efficient on viral protein production in specific cell types. These findings suggest that the H9N2/G1 virus like its counterpart H5N1/97 may be better adapted to the human host and replicates efficiently in human alveolar epithelial cells.
Figures
References
-
- Xu KM, Smith GJ, Bahl J, Duan L, Tai H, Vijaykrishna D, Wang J, Zhang JX, Li KS, Fan XH, Webster RG, Chen H, Peiris JS, Guan Y. The genesis and evolution of H9N2 influenza viruses in poultry from southern China, 2000 to 2005. J Virol. 2007;81:10389–10401. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00979-07. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lin YP, Shaw M, Gregory V, Cameron K, Lim W, Klimov A, Subbarao K, Guan Y, Krauss S, Shortridge K, Webster R, Cox N, Hay A. Avian-to-human transmission of H9N2 subtype influenza A viruses: relationship between H9N2 and H5N1 human isolates. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2000;97:9654–9658. doi: 10.1073/pnas.160270697. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

