A novel cross-talk in diacylglycerol signaling: the Rac-GAP beta2-chimaerin is negatively regulated by protein kinase Cdelta-mediated phosphorylation
- PMID: 20335173
- PMCID: PMC2878072
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.099036
A novel cross-talk in diacylglycerol signaling: the Rac-GAP beta2-chimaerin is negatively regulated by protein kinase Cdelta-mediated phosphorylation
Abstract
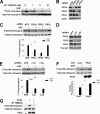
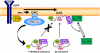
Although the family of chimaerin Rac-GAPs has recently gained significant attention for their involvement in development, cancer, and neuritogenesis, little is known about their molecular regulation. Chimaerins are activated by the lipid second messenger diacylglycerol via their C1 domain upon activation of tyrosine kinase receptors, thereby restricting the magnitude of Rac signaling in a receptor-regulated manner. Here we identified a novel regulatory mechanism for beta2-chimaerin via phosphorylation. Epidermal growth factor or the phorbol ester phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate caused rapid phosphorylation of beta2-chimaerin on Ser(169) located in the SH2-C1 domain linker region via protein kinase Cdelta, which retained beta2-chimaerin in the cytosol and prevented its C1 domain-mediated translocation to membranes. Furthermore, despite the fact that Ser(169) phosphorylation did not alter intrinsic Rac-GAP activity in vitro, a non-phosphorylatable beta2-chimaerin mutant was highly sensitive to translocation, and displayed enhanced association with activated Rac, enhanced Rac-GAP activity, and anti-migratory properties when expressed in cells. Our results not only revealed a novel regulatory mechanism that facilitates Rac activation, but also identified a novel mechanism of cross-talk between diacylglycerol receptors that restricts beta2-chimaerin relocalization and activation.
Figures

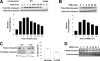





Similar articles
-
Identification of an autoinhibitory mechanism that restricts C1 domain-mediated activation of the Rac-GAP alpha2-chimaerin.J Biol Chem. 2008 Dec 12;283(50):35247-57. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M806264200. Epub 2008 Sep 30. J Biol Chem. 2008. PMID: 18826946 Free PMC article.
-
Coordinated activation of the Rac-GAP β2-chimaerin by an atypical proline-rich domain and diacylglycerol.Nat Commun. 2013;4:1849. doi: 10.1038/ncomms2834. Nat Commun. 2013. PMID: 23673634 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of the Rac-GAP (Rac-GTPase-activating protein) activity of beta2-chimaerin, a 'non-protein kinase C' phorbol ester receptor.Biochem J. 2003 Oct 15;375(Pt 2):313-21. doi: 10.1042/BJ20030727. Biochem J. 2003. PMID: 12877655 Free PMC article.
-
C1, see them all.Trends Biochem Sci. 2005 Apr;30(4):169-71. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2005.02.003. Trends Biochem Sci. 2005. PMID: 15817391 Review.
-
C1 domains exposed: from diacylglycerol binding to protein-protein interactions.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2006 Aug;1761(8):827-37. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2006.05.001. Epub 2006 May 13. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2006. PMID: 16861033 Review.
Cited by
-
PKC signaling in glioblastoma.Cancer Biol Ther. 2013 Apr;14(4):287-94. doi: 10.4161/cbt.23615. Epub 2013 Jan 28. Cancer Biol Ther. 2013. PMID: 23358475 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Post-Translational Modification and Subcellular Distribution of Rac1: An Update.Cells. 2018 Dec 11;7(12):263. doi: 10.3390/cells7120263. Cells. 2018. PMID: 30544910 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rho GTPases as therapeutic targets in cancer (Review).Int J Oncol. 2017 Oct;51(4):1025-1034. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2017.4093. Epub 2017 Aug 9. Int J Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28848995 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rac signaling in breast cancer: a tale of GEFs and GAPs.Cell Signal. 2012 Feb;24(2):353-362. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2011.08.011. Epub 2011 Aug 27. Cell Signal. 2012. PMID: 21893191 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PKCα phosphorylation of RhoGDI2 at Ser31 disrupts interactions with Rac1 and decreases GDI activity.Oncogene. 2013 Feb 21;32(8):1010-7. doi: 10.1038/onc.2012.124. Epub 2012 Apr 2. Oncogene. 2013. PMID: 22469974 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

