Protein-tyrosine phosphatase PTPN9 negatively regulates ErbB2 and epidermal growth factor receptor signaling in breast cancer cells
- PMID: 20335174
- PMCID: PMC2865303
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.099879
Protein-tyrosine phosphatase PTPN9 negatively regulates ErbB2 and epidermal growth factor receptor signaling in breast cancer cells
Abstract
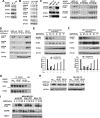
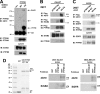
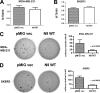
ErbB family of the receptor protein-tyrosine kinase plays an important role in the progression of human cancers including breast cancer. Finding protein-tyrosine phosphatase (PTPs) that can specifically regulate the function of ErbB should help design novel therapies for treatment. By performing a small interfering RNA screen against 43 human PTPs, we find that knockdown of protein-tyrosine phosphatase PTPN9 significantly increases ErbB2 tyrosyl phosphorylation in the SKBR3 breast cancer cell line. In addition, knockdown of PTPN9 expression also enhances tyrosyl phosphorylation of the ErbB1/epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) in the MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cell line. Conversely, increasing expression of PTPN9 wild type (WT) inhibits tyrosyl phosphorylation of ErbB2 and EGFR. To test whether ErbB2 and EGFR are substrates of PTPN9, PTPN9 WT, and a substrate trapping mutant (PTPN9 DA) are overexpressed in SKBR3 and MDA-MB-231 cells. Compared with vector control, expression of PTPN9 WT significantly inhibits whereas expression of PTPN9 DA dramatically enhances tyrosyl phosphorylation of ErbB2 and EGFR, respectively. In contrast, expression of PTPN9 WT or DA mutant does not affect tyrosyl phosphorylation of ErbB3 and Shc. Importantly, coimmunoprecipitation and glutathione S-transferase fusion protein pulldown experiments show that tyrosol-phosphorylated ErbB2 or EGFR is preferentially associated with PTPN9 DA compared with PTPN9 WT, indicating that ErbB2 and EGFR are substrates of PTPN9. Furthermore, PTPN9 WT expression specifically impairs EGF-induced STAT3 and STAT5 activation, and inhibits the cell growth in soft agar. Last, PTPN9 WT expression also reduces invasion and MMP2 expression of MDA-MB-231 cells. Our data suggest PTPN9 as a negative regulator of breast cancer cells by targeting ErbB2 and EGFR and inhibiting STAT activation.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Epidermal growth factor receptor, c-erbB2 and c-erbB3 receptor interaction, and related cell cycle kinetics of SK-BR-3 and BT474 breast carcinoma cells.Cytometry. 2001 Aug 1;44(4):338-48. doi: 10.1002/1097-0320(20010801)44:4<338::aid-cyto1125>3.0.co;2-v. Cytometry. 2001. PMID: 11500850
-
Flotillin depletion affects ErbB protein levels in different human breast cancer cells.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014 Sep;1843(9):1987-96. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2014.04.013. Epub 2014 Apr 18. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014. PMID: 24747692
-
MicroRNA miR-24 enhances tumor invasion and metastasis by targeting PTPN9 and PTPRF to promote EGF signaling.J Cell Sci. 2013 Mar 15;126(Pt 6):1440-53. doi: 10.1242/jcs.118299. Epub 2013 Feb 15. J Cell Sci. 2013. PMID: 23418360
-
Targeting of ErbB1, ErbB2, and their Dual Targeting Using Small Molecules and Natural Peptides: Blocking EGFR Cell Signaling Pathways in Cancer: A Mini-Review.Mini Rev Med Chem. 2022 Oct 21;22(22):2831-2846. doi: 10.2174/1389557522666220512152448. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2022. PMID: 35549881 Review.
-
ErbB Receptors and Cancer.Methods Mol Biol. 2017;1652:3-35. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-7219-7_1. Methods Mol Biol. 2017. PMID: 28791631 Review.
Cited by
-
MiR-96 enhances cellular proliferation and tumorigenicity of human cervical carcinoma cells through PTPN9.Saudi J Biol Sci. 2018 Jul;25(5):863-867. doi: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2017.10.020. Epub 2018 Feb 7. Saudi J Biol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30108433 Free PMC article.
-
Protein tyrosine phosphatases in cell adhesion.Biochem J. 2021 Mar 12;478(5):1061-1083. doi: 10.1042/BCJ20200511. Biochem J. 2021. PMID: 33710332 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Signal transducer and activator of transcription 5 as a key signaling pathway in normal mammary gland developmental biology and breast cancer.Breast Cancer Res. 2011 Oct 12;13(5):220. doi: 10.1186/bcr2921. Breast Cancer Res. 2011. PMID: 22018398 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MEG2 is regulated by miR-181a-5p and functions as a tumour suppressor gene to suppress the proliferation and migration of gastric cancer cells.Mol Cancer. 2017 Jul 26;16(1):133. doi: 10.1186/s12943-017-0695-7. Mol Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28747184 Free PMC article.
-
CircMMD_007 promotes oncogenic effects in the progression of lung adenocarcinoma through microRNA-197-3p/protein tyrosine phosphatase non-receptor type 9 axis.Bioengineered. 2022 Mar;13(3):4991-5004. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2022.2037956. Bioengineered. 2022. PMID: 35156900 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

