The FoxF/FoxC factor LET-381 directly regulates both cell fate specification and cell differentiation in C. elegans mesoderm development
- PMID: 20335356
- PMCID: PMC2853847
- DOI: 10.1242/dev.048496
The FoxF/FoxC factor LET-381 directly regulates both cell fate specification and cell differentiation in C. elegans mesoderm development
Abstract
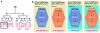
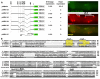
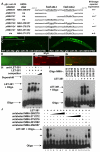
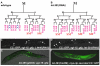
Forkhead transcription factors play crucial and diverse roles in mesoderm development. In particular, FoxF and FoxC genes are, respectively, involved in the development of visceral/splanchnic mesoderm and non-visceral mesoderm in coelomate animals. Here, we show at single-cell resolution that, in the pseudocoelomate nematode C. elegans, the single FoxF/FoxC transcription factor LET-381 functions in a feed-forward mechanism in the specification and differentiation of the non-muscle mesodermal cells, the coelomocytes (CCs). LET-381/FoxF directly activates the CC specification factor, the Six2 homeodomain protein CEH-34, and functions cooperatively with CEH-34/Six2 to directly activate genes required for CC differentiation. Our results unify a diverse set of studies on the functions of FoxF/FoxC factors and provide a model for how FoxF/FoxC factors function during mesoderm development.
Figures


References
-
- Amin N. M., Hu K., Pruyne D., Terzic D., Bretscher A., Liu J. (2007). A Zn-finger/FH2-domain containing protein, FOZI-1, acts redundantly with CeMyoD to specify striated body wall muscle fates in the Caenorhabditis elegans postembryonic mesoderm. Development 134, 19-29 - PubMed
-
- Beh J., Shi W., Levine M., Davidson B., Christiaen L. (2007). FoxF is essential for FGF-induced migration of heart progenitor cells in the ascidian Ciona intestinalis. Development 134, 3297-3305 - PubMed
-
- Brown C. D., Johnson D. S., Sidow A. (2007). Functional architecture and evolution of transcriptional elements that drive gene coexpression. Science 317, 1557-1560 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

