Identification of hydroxyxanthones as Na/K-ATPase ligands
- PMID: 20335388
- PMCID: PMC2879917
- DOI: 10.1124/mol.110.063974
Identification of hydroxyxanthones as Na/K-ATPase ligands
Abstract
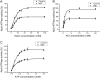
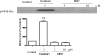
We have screened a chemical library and identified several novel structures of Na/K-ATPase inhibitors. One group of these inhibitors belongs to polyphenolic xanthone derivatives. Functional characterization reveals the following properties of this group of inhibitors. First, like ouabain, they are potent inhibitors of the purified Na/K-ATPase. Second, their effects on the Na/K-ATPase depend on the number and position of phenolic groups. Methylation of these phenolic groups reduces the inhibitory effect. Third, further characterization of the most potent xanthone derivative, MB7 (3,4,5,6-tetrahydroxyxanthone), reveals that it does not change either Na(+) or ATP affinity of the enzyme. Finally, unlike that of ouabain, the inhibitory effect of MB7 on Na/K-ATPase is not antagonized by K(+). Moreover, MB7 does not activate the receptor Na/K-ATPase/Src complex and fails to stimulate protein kinase cascades in cultured cells. Thus, we have identified a group of novel Na/K-ATPase ligands that can inhibit the pumping function without stimulating the signaling function of Na/K-ATPase.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Involvement of Na/K-ATPase in hydrogen peroxide-induced activation of the Src/ERK pathway in LLC-PK1 cells.Free Radic Biol Med. 2014 Jun;71:415-426. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2014.03.036. Epub 2014 Apr 1. Free Radic Biol Med. 2014. PMID: 24703895 Free PMC article.
-
Heterogeneity of signal transduction by Na-K-ATPase α-isoforms: role of Src interaction.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2018 Feb 1;314(2):C202-C210. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00124.2017. Epub 2017 Nov 8. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29118027 Free PMC article.
-
Ouabain-induced endocytosis of the plasmalemmal Na/K-ATPase in LLC-PK1 cells requires caveolin-1.Kidney Int. 2005 May;67(5):1844-54. doi: 10.1111/j.1523-1755.2005.00283.x. Kidney Int. 2005. PMID: 15840032
-
Ouabain-induced endocytosis and signal transduction of the Na/K-ATPase.Front Biosci. 2005 Sep 1;10:2056-63. doi: 10.2741/1681. Front Biosci. 2005. PMID: 15970478 Review.
-
Molecular mechanisms of Na/K-ATPase-mediated signal transduction.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2003 Apr;986:497-503. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2003.tb07234.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2003. PMID: 12763870 Review.
Cited by
-
Inverse agonism at the Na/K-ATPase receptor reverses EMT in prostate cancer cells.Prostate. 2021 Jul;81(10):667-682. doi: 10.1002/pros.24144. Epub 2021 May 6. Prostate. 2021. PMID: 33956349 Free PMC article.
-
Synthetic Naphthoquinone Inhibits Herpes Simplex Virus Type-1 Replication Targeting Na+, K+ ATPase.ACS Omega. 2024 Aug 16;9(34):36835-36846. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.4c05904. eCollection 2024 Aug 27. ACS Omega. 2024. PMID: 39220530 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiac glycoside activities link Na(+)/K(+) ATPase ion-transport to breast cancer cell migration via correlative SAR.ACS Chem Biol. 2015 Feb 20;10(2):561-9. doi: 10.1021/cb500665r. Epub 2014 Nov 26. ACS Chem Biol. 2015. PMID: 25334087 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of renal function and structure by the signaling Na/K-ATPase.IUBMB Life. 2013 Dec;65(12):991-8. doi: 10.1002/iub.1229. Epub 2013 Dec 10. IUBMB Life. 2013. PMID: 24323927 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Complementary Chemical and Genomic Screening Approach for Druggable Targets in the Nrf2 Pathway and Small Molecule Inhibitors to Overcome Cancer Cell Drug Resistance.ACS Chem Biol. 2018 May 18;13(5):1189-1199. doi: 10.1021/acschembio.7b01025. Epub 2018 Mar 22. ACS Chem Biol. 2018. PMID: 29565554 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akera T, Brody TM. (1976) Inotropic action of digitalis and ion transport. Life Sci 18:135–144 - PubMed
-
- Aydemir-Koksoy A, Abramowitz J, Allen JC. (2001) Ouabain-induced signaling and vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation. J Biol Chem 276:46605–46611 - PubMed
-
- Bagrov AY, Fedorova OV. (1998) Effects of two putative endogenous digitalis-like factors, marinobufagenin and ouabain, on the Na+, K+ pump in human mesenteric arteries. J Hypertens 16:1953–1958 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

