The functional properties of barrel cortex neurons projecting to the primary motor cortex
- PMID: 20335461
- PMCID: PMC6634518
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3774-09.2010
The functional properties of barrel cortex neurons projecting to the primary motor cortex
Abstract
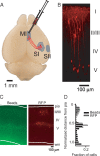
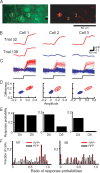
Nearby neurons, sharing the same locations within the mouse whisker map, can have dramatically distinct response properties. To understand the significance of this diversity, we studied the relationship between the responses of individual neurons and their projection targets in the mouse barrel cortex. Neurons projecting to primary motor cortex (MI) or secondary somatosensory area (SII) were labeled with red fluorescent protein (RFP) using retrograde viral infection. We used in vivo two-photon Ca(2+) imaging to map the responses of RFP-positive and neighboring L2/3 neurons to whisker deflections. Neurons projecting to MI displayed larger receptive fields compared with other neurons, including those projecting to SII. Our findings support the view that intermingled neurons in primary sensory areas send specific stimulus features to different parts of the brain.
Figures
References
-
- Alloway KD. Information processing streams in rodent barrel cortex: The differential functions of barrel and septal circuits. Cereb Cortex. 2008;18:979–989. - PubMed
-
- Armstrong-James M, Fox K. Spatiotemporal convergence and divergence in the rat S1 “barrel” cortex. J Comp Neurol. 1987;263:265–281. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
