Endogenous purinergic control of bladder activity via presynaptic P2X3 and P2X2/3 receptors in the spinal cord
- PMID: 20335487
- PMCID: PMC2882023
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.6132-09.2010
Endogenous purinergic control of bladder activity via presynaptic P2X3 and P2X2/3 receptors in the spinal cord
Abstract
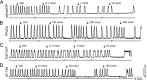
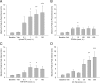
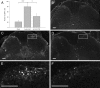
P2X(3) and P2X(2/3) receptors are localized on sensory afferents both peripherally and centrally and have been implicated in various sensory functions. However, the physiological role of these receptors expressed presynaptically in the spinal cord in regulating sensory transmission remains to be elucidated. Here, a novel selective P2X(3) and P2X(2/3) antagonist, AF-792 [5-(5-ethynyl-2-isopropyl-4-methoxy-phenoxy)-pyrimidine-2,4-diamine, previously known as RO-5], in addition to less selective purinoceptor ligands, was applied intrathecally in vivo. Cystometry recordings were made to assess changes in the micturition reflex contractions after drug treatments. We found that AF-792 inhibited micturition reflex activity significantly (300 nmol; from baseline contraction intervals of 1.18 +/- 0.07 to 9.33 +/- 2.50 min). Furthermore, inhibition of P2X(3) and P2X(2/3) receptors in the spinal cord significantly attenuated spinal activation of extracellular-signal regulated kinases induced by acute peripheral stimulation of the bladder with 1% acetic acid by 46.4 +/- 12.0% on average. Hence, the data suggest that afferent signals originating from the bladder are regulated by spinal P2X(3) and P2X(2/3) receptors and establish directly an endogenous central presynaptic purinergic mechanism to regulate visceral sensory transmission. Identification of this spinal purinergic control in visceral activities may help the development of P2X(3) and P2X(2/3) antagonist to treat urological dysfunction, such as overactive bladder, and possibly other debilitating sensory disorders, including chronic pain states.
Figures
References
-
- Avelino A, Cruz F, Coimbra A. Intravesical resiniferatoxin desensitizes rat bladder sensory fibres without causing intense noxious excitation. A c-fos study. Eur J Pharmacol. 1999;378:17–22. - PubMed
-
- Bradbury EJ, Burnstock G, McMahon SB. The expression of P2X3 purinoreceptors in sensory neurons: effects of axotomy and glial-derived neurotrophic factor. Mol Cell Neurosci. 1998;12:256–268. - PubMed
-
- Carter DS, Alam M, Cai H, Dillon MP, Ford AP, Gever JR, Jahangir A, Lin C, Moore AG, Wagner PJ, Zhai Y. Identification and SAR of novel diaminopyrimidines. Part 1. The discovery of RO-4, a dual P2X3/P2X2/3 antagonist for the treatment of pain. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2009;19:1628–1631. - PubMed
-
- Cefalu JS, Burbach LR, Guillon MA, Benham JJ, Cockayne DA, Ford AP, Nunn PA. Comparison of novel high and low central nervous system penetrating dual purinergic P2X3/P2X2/3 antagonists on the micturition reflex in anesthetized rats. Paper presented at the American Urological Association Annual Meeting; May; Anaheim, CA. 2007a.
-
- Cefalu JS, Zhu QM, Eggers AC, Kaan TK, Ho MJ, Jett MF, Cockayne DA, Ford AP, Nunn PA. Effects of the selective prostacyclin receptor antagonist RO3244019 on the micturition reflex in rats. J Urol. 2007b;178:2683–2688. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
