Metabolic cycling in single yeast cells from unsynchronized steady-state populations limited on glucose or phosphate
- PMID: 20335538
- PMCID: PMC2872461
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1002422107
Metabolic cycling in single yeast cells from unsynchronized steady-state populations limited on glucose or phosphate
Erratum in
- Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011 Jul 19;108(29):12185
Abstract
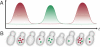
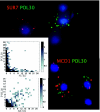
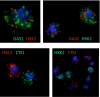
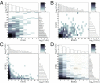
Oscillations in patterns of expression of a large fraction of yeast genes are associated with the "metabolic cycle," usually seen only in prestarved, continuous cultures of yeast. We used FISH of mRNA in individual cells to test the hypothesis that these oscillations happen in single cells drawn from unsynchronized cultures growing exponentially in chemostats. Gene-expression data from synchronized cultures were used to predict coincident appearance of mRNAs from pairs of genes in the unsynchronized cells. Quantitative analysis of the FISH results shows that individual unsynchronized cells growing slowly because of glucose limitation or phosphate limitation show the predicted oscillations. We conclude that the yeast metabolic cycle is an intrinsic property of yeast metabolism and does not depend on either synchronization or external limitation of growth by the carbon source.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Ghosh AK, Chance B, Pye EK. Metabolic coupling and synchronization of NADH oscillations in yeast cell populations. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1971;145:319–331. - PubMed
-
- Tu BP, Kudlicki A, Rowicka M, McKnight SL. Logic of the yeast metabolic cycle: Temporal compartmentalization of cellular processes. Science. 2005;310:1152–1158. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

