Synthesis, spectral and thermal studies of new rutin vanadyl complexes
- PMID: 20336002
- PMCID: PMC6257295
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules15031578
Synthesis, spectral and thermal studies of new rutin vanadyl complexes
Abstract
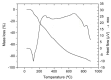
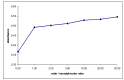
Complexes between oxovanadium (IV) cation and flavonoid derivatives were developed recently in order to increase the intestinal absorption and to reduce the toxicity of vanadium compounds. For these reasons, is interesting to investigate the complexation process between flavonoid rutin (Rut) and vanadyl cation in order to isolate new complexes. Two new complexes [VO(Rut)(H2O)2](SO4)0.5 x 2 H2O and [VO(Rut)2] x 4 H2O have been obtained and characterized by elemental and thermal analyses and several spectroscopic techniques (ESI-MS, IR, UV-Vis, fluorescence). The studies concerning complex formation between vanadyl and rutin (Rut) performed in different solutions show the formation of mononuclear complexes with 1:1 and 1:2 metal to ligand stoichiometry.
Figures







References
-
- Nijveldt R.J., van Nood E., van Hoorn D.E.C., Boelens P.G., van Norren K., van Leeuwen P.A.M. Flavonoids: A review of probable mechanisms of action and potential applications. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2001;74:418–425. - PubMed
-
- Kris-Etherton P.M., Hecker K.D., Bonanome A., Coval S.M., Binkoski A.E., Hilpert K.F., Griel A.E., Etherton T.D. Bioactive compounds in foods: Their role in the prevention of cardiovascular disease and cancer. Am. J. Med. 2002;113:71–88. - PubMed
-
- Manach C., Regerat F, Texier O., Agullo G., Demigne C., Remesy C. Bioavailability, metabolism and physiological impact of 4-oxo-flavonoids. Nutr. Res. 1996;16:517–544.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

