The molecular mechanism of action of artemisinin--the debate continues
- PMID: 20336009
- PMCID: PMC6257357
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules15031705
The molecular mechanism of action of artemisinin--the debate continues
Abstract
Despite international efforts to 'roll back malaria' the 2008 World Malaria Report revealed the disease still affects approximately 3 billion people in 109 countries; 45 within the WHO African region. The latest report however does provide some 'cautious optimism'; more than one third of malarious countries have documented greater than 50% reductions in malaria cases in 2008 compared to 2000. The goal of the Member States at the World Health Assembly and 'Roll Back Malaria' (RBM) partnership is to reduce the numbers of malaria cases and deaths recorded in 2000 by 50% or more by the end of 2010. Although malaria is preventable it is most prevalent in poorer countries where prevention is difficult and prophylaxis is generally not an option. The burden of disease has increased by the emergence of multi drug resistant (MDR) parasites which threatens the use of established and cost effective antimalarial agents. After a major change in treatment policies, artemisinins are now the frontline treatment to aid rapid clearance of parasitaemia and quick resolution of symptoms. Since artemisinin and its derivatives are eliminated rapidly, artemisinin combination therapies (ACT's) are now recommended to delay resistance mechanisms. In spite of these precautionary measures reduced susceptibility of parasites to the artemisinin-based component of ACT's has developed at the Thai-Cambodian border, a historical 'hot spot' for MDR parasite evolution and emergence. This development raises serious concerns for the future of the artemsinins and this is not helped by controversy related to the mode of action. Although a number of potential targets have been proposed the actual mechanism of action remains ambiguous. Interestingly, artemisinins have also shown potent and broad anticancer properties in cell lines and animal models and are becoming established as anti-schistosomal agents. In this review we will discuss the recent evidence explaining bioactivation and potential molecular targets in the chemotherapy of malaria and cancer.
Figures

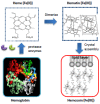

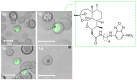

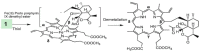

References
-
- World Heath Organisation . The World Malaria Report. World Heath Organisation; Geneva, Switzerland: 2008.
-
- Zhang J.-F. Yang Cheng Evening News Publishing Company; 2005. A Detailed Chronological Record of Project 523 and the Discovery and Development of Qinghaosu (Artemisinin)
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

