How are T(H)2-type immune responses initiated and amplified?
- PMID: 20336151
- PMCID: PMC3496776
- DOI: 10.1038/nri2735
How are T(H)2-type immune responses initiated and amplified?
Abstract
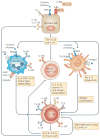
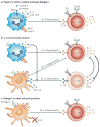
CD4(+) T helper (T(H)) cells have crucial roles in orchestrating adaptive immune responses. T(H)2 cells control immunity to extracellular parasites and all forms of allergic inflammatory responses. Although we understand the initiation of the T(H)2-type response in tissue culture in great detail, much less is known about T(H)2 cell induction in vivo. Here we discuss the involvement of allergen- and parasite product-mediated activation of epithelial cells, basophils and dendritic cells and the functions of the cytokines interleukin-4 (IL-4), IL-25, IL-33 and thymic stromal lymphopoietin in the initiation and amplification of T(H)2-type immune responses in vivo.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures

References
-
- Pestka S, et al. Interleukin-10 and related cytokines and receptors. Annu Rev Immunol. 2004;22:929–979. - PubMed
-
- Couper KN, Blount DG, Riley EM. IL-10: the master regulator of immunity to infection. J Immunol. 2008;180:5771–5777. - PubMed
-
- Spolski R, Leonard WJ. Interleukin-21: basic biology and implications for cancer and autoimmunity. Annu Rev Immunol. 2008;26:57–79. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

