Role of Radiation-induced TGF-beta Signaling in Cancer Therapy
- PMID: 20336170
- PMCID: PMC2844640
- DOI: 10.4255/mcpharmacol.09.06
Role of Radiation-induced TGF-beta Signaling in Cancer Therapy
Abstract
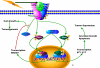
TGF-β signaling regulates several different biological processes involving cell-growth, differentiation, apoptosis, motility, angiogenesis, epithelial mesenchymal transition and extracellular matrix production that affects embryonic development and pathogenesis of various diseases, including cancer, its effects depending on the cellular context and physiological environment. Growth suppression mediated by TGF-β signaling often associated with inhibition of c-myc, cdks and induction of p15, p27, Bax and p21. Despite its growth inhibitory effect, in certain conditions TGF-β may act as a promoter of cell proliferation and invasion. Loss of responsiveness to growth suppression by TGF-β due to mutation or loss of TGF-beta type II receptor (TβRII) and Smad4 in several different cancer cells are reported. In addition, TGF-β binding to its receptor activates many non-canonical signaling pathways. Radiation induced TGF-β is primarily involved in normal tissue injury and fibrosis. Seminal studies from our group have used radio-adjuvant therapies, involving classical components of the pathway such as TβRII and SMAD4 to overcome the growth promoting effects of TGF-β. The main impediment in the radiation-induced TGF-β signaling is the induction of SMAD7 that blocks TGF-β signaling in a negative feedback manner. It is well demonstrated from our studies that the use of neutralizing antibodies against TGF- β can render a robust radio-resistant effect. Thus, understanding the functional interactions of TGF-β signaling components of the pathway with other molecules may help tailor appropriate adjuvant radio-therapeutic strategies for treatment of solid tumors.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase by TGF-beta1 via TbetaRII and Smad7 dependent mechanisms in human bronchial epithelial BEP2D cells.Cell Biol Toxicol. 2007 Mar;23(2):113-28. doi: 10.1007/s10565-006-0097-x. Epub 2006 Nov 9. Cell Biol Toxicol. 2007. PMID: 17096210
-
An epigenetic auto-feedback loop regulates TGF-β type II receptor expression and function in NSCLC.Oncotarget. 2015 Oct 20;6(32):33237-52. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.4893. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 26356817 Free PMC article.
-
Restoration of transforming growth factor beta signaling pathway in human prostate cancer cells suppresses tumorigenicity via induction of caspase-1-mediated apoptosis.Cancer Res. 1999 Mar 15;59(6):1366-71. Cancer Res. 1999. PMID: 10096572
-
Regulation of TGF-beta signaling by Smad7.Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2009 Apr;41(4):263-72. doi: 10.1093/abbs/gmp018. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2009. PMID: 19352540 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploring the potential of TGFβ as a diagnostic marker and therapeutic target against cancer.Biochem Pharmacol. 2025 Jan;231:116646. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2024.116646. Epub 2024 Nov 20. Biochem Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39577704 Review.
Cited by
-
MicroRNA and signal transduction pathways in tumor radiation response.Cell Signal. 2013 Jul;25(7):1625-34. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2013.04.004. Epub 2013 Apr 17. Cell Signal. 2013. PMID: 23602933 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibition of TGF-β signaling with halofuginone can enhance the antitumor effect of irradiation in Lewis lung cancer.Onco Targets Ther. 2015 Dec 2;8:3549-59. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S92518. eCollection 2015. Onco Targets Ther. 2015. PMID: 26664138 Free PMC article.
-
Combining Radiation Therapy with Immune Checkpoint Blockade for Central Nervous System Malignancies.Front Oncol. 2016 Oct 7;6:212. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2016.00212. eCollection 2016. Front Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27774435 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chemoradiation induces epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in esophageal adenocarcinoma.Int J Cancer. 2019 Nov 15;145(10):2792-2803. doi: 10.1002/ijc.32364. Epub 2019 May 7. Int J Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31018252 Free PMC article.
-
Overexpression of MLPH in Rectal Cancer Patients Correlates with a Poorer Response to Preoperative Chemoradiotherapy and Reduced Patient Survival.Diagnostics (Basel). 2021 Nov 17;11(11):2132. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics11112132. Diagnostics (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34829479 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Massague J. A very private TGF-beta receptor embrace. Mol Cell. 2008;29:149–50. - PubMed
-
- Petrocca F, Visone R, Onelli MR, et al. E2F1-regulated microRNAs impair TGFbeta-dependent cell-cycle arrest and apoptosis in gastric cancer. Cancer Cell. 2008;13:272–86. - PubMed
-
- Martin M, Lefaix J, Delanian S. TGF-beta1 and radiation fibrosis: a master switch and a specific therapeutic target? Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2000;47:277–90. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
