Capillary array isoelectric focusing with laser-induced fluorescence detection: milli-pH unit resolution and yoctomole mass detection limits in a 32-channel system
- PMID: 20336452
- PMCID: PMC3252051
- DOI: 10.1007/s00216-010-3595-x
Capillary array isoelectric focusing with laser-induced fluorescence detection: milli-pH unit resolution and yoctomole mass detection limits in a 32-channel system
Abstract
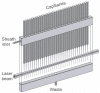
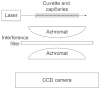
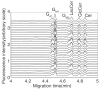
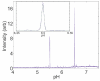
We report a multiplexed capillary electrophoresis system employing an array of 32 capillaries with a micromachined sheath-flow cuvette as the detection chamber. The sample streams were simultaneously excited with a 473-nm laser beam, and the fluorescence emission was imaged on a CCD camera with a pair of doublet achromat lens. The instrument produced mass detection limits of 380 +/- 120 yoctomoles for fluorescein in zone electrophoresis. Capillary isoelectric focusing of fluorescent standards produced peaks with an average width of 0.0029 +/- 0.0008 pH. Capillary coating stability limits the reproducibility of the analysis.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Femtomolar concentration detection limit and zeptomole mass detection limit for protein separation by capillary isoelectric focusing and laser-induced fluorescence detection.Anal Chem. 2009 Mar 1;81(5):1741-6. doi: 10.1021/ac8025948. Anal Chem. 2009. PMID: 19206532 Free PMC article.
-
Two-dimensional capillary electrophoresis: capillary isoelectric focusing and capillary zone electrophoresis with laser-induced fluorescence detection.Electrophoresis. 2010 Aug;31(15):2650-4. doi: 10.1002/elps.201000151. Electrophoresis. 2010. PMID: 20603830 Free PMC article.
-
Fluorescence imaging detection for capillary isoelectric focusing.Electrophoresis. 1995 Aug;16(8):1474-8. doi: 10.1002/elps.11501601244. Electrophoresis. 1995. PMID: 8529617
-
Recent developments in capillary isoelectric focusing with whole-column imaging detection.Electrophoresis. 1998 Oct;19(13):2290-5. doi: 10.1002/elps.1150191307. Electrophoresis. 1998. PMID: 9788311 Review.
-
Conventional isoelectric focusing. In gel slabs and capillaries and immobilized pH gradients.Methods Biochem Anal. 2011;54:379-409. doi: 10.1002/9780470939932.ch16. Methods Biochem Anal. 2011. PMID: 21954787 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Capillary isoelectric focusing with pH 9.7 cathode for the analysis of gastric biopsies.Anal Bioanal Chem. 2011 Jun;400(7):2025-30. doi: 10.1007/s00216-011-4926-2. Epub 2011 Apr 2. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2011. PMID: 21461616 Free PMC article.
-
Capillary isoelectric focusing of individual mitochondria.Anal Chem. 2011 Jan 15;83(2):612-8. doi: 10.1021/ac102712r. Epub 2010 Dec 30. Anal Chem. 2011. PMID: 21192658 Free PMC article.
-
Application of Capillary Electrophoresis with Laser-Induced Fluorescence to Immunoassays and Enzyme Assays.Molecules. 2019 May 22;24(10):1977. doi: 10.3390/molecules24101977. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 31121978 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Capillary isoelectric focusing-tandem mass spectrometry and reversed-phase liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry for quantitative proteomic analysis of differentiating PC12 cells by eight-plex isobaric tags for relative and absolute quantification.Anal Chem. 2013 Aug 6;85(15):7221-9. doi: 10.1021/ac4009868. Epub 2013 Jul 18. Anal Chem. 2013. PMID: 23822771 Free PMC article.
-
On-line amino acid-based capillary isoelectric focusing-ESI-MS/MS for protein digests analysis.Anal Chim Acta. 2012 Oct 31;750:207-11. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2012.04.026. Epub 2012 Apr 27. Anal Chim Acta. 2012. PMID: 23062442 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Righetti PG. Isoelectric Focusing: Theory, Methodology and Applications. Elsevier; Amsterdam: 1983.
-
- Righetti PG. Immobilized pH Gradients: Theory and Methodology. Elsevier; Amsterdam: 1990.
-
- Cossu G, Righetti PG. Resolution Of γ-Gamma and α-Gamma Fetal Hemoglobin Tetramers in Immobilized pH Gradients. J Chromatogr. 1987;398:211–216. - PubMed
-
- Wu JQ, Pawliszyn J. Capillary Isoelectric-Focusing With A Universal Concentration Gradient Imaging-System Using A Charge-Coupled Photodiode Array. Anal Chem. 1992;64:2934–2941.
-
- Wu J, Pawliszyn J. Fast analysis of proteins by isoelectric focusing performed in capillary array detected with concentration gradient imaging system. Electrophoresis. 1993;14:469–474. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

