Shaping development of autophagy inhibitors with the structure of the lipid kinase Vps34
- PMID: 20339072
- PMCID: PMC2860105
- DOI: 10.1126/science.1184429
Shaping development of autophagy inhibitors with the structure of the lipid kinase Vps34
Abstract
Phosphoinositide 3-kinases (PI3Ks) are lipid kinases with diverse roles in health and disease. The primordial PI3K, Vps34, is present in all eukaryotes and has essential roles in autophagy, membrane trafficking, and cell signaling. We solved the crystal structure of Vps34 at 2.9 angstrom resolution, which revealed a constricted adenine-binding pocket, suggesting the reason that specific inhibitors of this class of PI3K have proven elusive. Both the phosphoinositide-binding loop and the carboxyl-terminal helix of Vps34 mediate catalysis on membranes and suppress futile adenosine triphosphatase cycles. Vps34 appears to alternate between a closed cytosolic form and an open form on the membrane. Structures of Vps34 complexes with a series of inhibitors reveal the reason that an autophagy inhibitor preferentially inhibits Vps34 and underpin the development of new potent and specific Vps34 inhibitors.
Figures


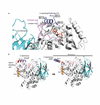
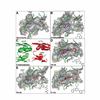
Comment in
-
Unveiling the secrets of the ancestral PI3 kinase Vps34.Cancer Cell. 2010 May 18;17(5):421-3. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2010.04.016. Cancer Cell. 2010. PMID: 20478524
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

