Toll-like receptor 9 signaling by CpG-B oligodeoxynucleotides induces an apoptotic pathway in human chronic lymphocytic leukemia B cells
- PMID: 20339095
- PMCID: PMC2890142
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2009-03-213363
Toll-like receptor 9 signaling by CpG-B oligodeoxynucleotides induces an apoptotic pathway in human chronic lymphocytic leukemia B cells
Abstract
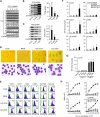
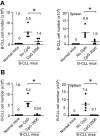
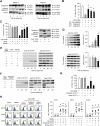
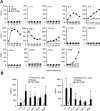
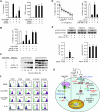
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) is the most prevalent human leukemia and is characterized by the progressive accumulation of long-lived malignant B cells. Here we show that human B-CLL cells selectively express high levels of Toll-like receptor 9 (TLR9) mRNA and proteins. Treating B-CLL cells with TLR9 agonists, type B CpG oligodeoxynucleotides (CpG-B ODNs), induces significant morphologic and phenotypic activation, altered cytokine production, reversal of signal transducer, and activator of transcription 1 (STAT1) phosphorylation state, followed by profound apoptosis of B-CLL cells that is CpG-B ODN treatment time- and dose-dependent. TLR9-CpG ODN ligation-induced apoptosis of B-CLL cells is confirmed by viable cell counts, annexin V/propidium iodide and tetramethyl-rhodamine ethylester staining, Western blots of the activation, and cleaved caspases and poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase. Triggering TLR9 by CpG-B ODN leads to nuclear factor-kappaB-dependent production of autocrine interleukin-10, which activates JAK/STAT pathway-dependent tyrosine phosphorylation of STAT1 proteins and thereby provokes an apoptosis pathway in B-CLL cells. Treating B-CLL cells in vitro or in vivo with CpG-B ODN reduces the number of leukemia cells that engraft in NOD-scid mice. These findings provide new understanding of CpG ODN-mediated antitumor effects and support for the development of TLR9-targeted therapy for human CLL.
Figures

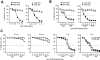
References
-
- O'Brien S, del Giglio A, Keating M. Advances in the biology and treatment of B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood. 1995;85(2):307–318. - PubMed
-
- Döhner H, Stilgenbauer S, Benner A, et al. Genomic aberrations and survival in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2000;343(26):1910–1916. - PubMed
-
- Rassenti LZ, Huynh L, Toy TL, et al. ZAP-70 compared with immunoglobulin heavy-chain gene mutation status as a predictor of disease progression in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2004;351(9):893–901. - PubMed
-
- Montserrat E, Moreno C, Esteve J, Urbano-Ispizua A, Gine E, Bosch F. How I treat refractory CLL. Blood. 2006;107(4):1276–1283. - PubMed
-
- Hallek M, Cheson BD, Catovsky D, et al. Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukemia: a report from the International Workshop on Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia updating the National Cancer Institute-Working Group 1996 guidelines. Blood. 2008;111(12):5446–5456. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

