Segmental tissue Doppler image-derived tei index in patients with regional wall motion abnormalities
- PMID: 20339495
- PMCID: PMC2844976
- DOI: 10.4070/kcj.2010.40.3.114
Segmental tissue Doppler image-derived tei index in patients with regional wall motion abnormalities
Abstract
Background and objectives: Although the Tei index is a useful predictor of global ventricular function, it has not been investigated at the level of regional myocardial function. We therefore investigated the segmental tissue Doppler image derived-Tei index (TDI-Tei index) in patients with regional wall motion abnormalities.
Subjects and methods: We prospectively studied 17 patients (mean age 62+/-9 years, 5 women) with left ventricular (LV) regional wall motion abnormalities. The Tei index, defined as the sum of isovolumetric contraction time (IVCT) and isovolumetric relaxation time (IVRT) divided by ejection time (ET), was measured in the basal and mid segments of the LV walls from standard apical views (4-, 2-, and 5-chamber views). We also obtained TDI velocity data in each segment. LV wall motion was classified as normal, hypokinetic, or akinetic, based on visual analysis. The TDI-Tei index, peak systolic myocardial velocity (Sm), early diastolic myocardial velocity (Em), and late diastolic myocardial velocity (Am) were analyzed in a total of 203 segments.
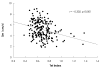
Results: Mean LV ejection fraction was 41.8+/-8.5%. TDI-Tei indices of dysfunctional segments (akinesis or hypokinesis, n=63) were significantly higher than those of normal segments (n=140) (0.714+/-0.169 vs. 0.669+/-0.135, p=0.041, respectively). Average values of TDI-Tei index, Sm, Em, and Am were 0.742+/-0.201, 4.206+/-1.336, 5.258+/-1.867, and 5.578+/-2.354 in akinetic segments; 0.677+/-0.101, 4.908+/-1.615, 5.369+/-2.121, and 5.542+/-2.492 in hypokinetic segments; and 0.669+/-0.135, 5.409+/-1.519, 6.108+/-2.356, and 6.719+/-2.466 in normal segments, respectively. A significant negative correlation was apparent between the TDI-Tei index and Sm (r=-0.302, p<0.001).
Conclusion: These data suggest that the value of the segmental TDI-Tei index differs significantly according to regional function grade.
Keywords: Echocardiograph, Doppler; Myocardial contraction; Ventricular function.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Assessment of left ventricular diastolic function and the Tei index by tissue Doppler imaging in patients with primary hyperparathyroidism.Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2007 Apr;66(4):483-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2265.2007.02756.x. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2007. PMID: 17371463
-
Assessment of left ventricular function and Tei index by tissue Doppler imaging in patients with slow coronary flow.Echocardiography. 2009 Nov;26(10):1167-72. doi: 10.1111/j.1540-8175.2009.00939.x. Epub 2009 Aug 28. Echocardiography. 2009. PMID: 19725862
-
Comparison of the tissue Doppler-derived left ventricular Tei index to that obtained by pulse Doppler in patients with congenital and acquired heart disease.Pediatr Cardiol. 2005 Jul-Aug;26(4):391-5. doi: 10.1007/s00246-004-0757-7. Pediatr Cardiol. 2005. PMID: 16374688
-
Assessment of the Tei index by tissue Doppler imaging in patients with acromegaly: serum growth hormone level is associated with the Tei index.Echocardiography. 2008 Apr;25(4):374-80. doi: 10.1111/j.1540-8175.2007.00615.x. Epub 2008 Jan 3. Echocardiography. 2008. PMID: 18177382
-
Assessment of left ventricular diastolic function and Tei index by tissue Doppler imaging in patients with Cushing's Syndrome.Echocardiography. 2008 Feb;25(2):182-90. doi: 10.1111/j.1540-8175.2007.00572.x. Echocardiography. 2008. PMID: 18269563
Cited by
-
Dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging in patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension.Pulm Circ. 2014 Mar;4(1):61-70. doi: 10.1086/674882. Pulm Circ. 2014. PMID: 25006422 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tei C. New non-invasive index for combined systolic and diastolic ventricular function. J Cardiol. 1995;26:135–136. - PubMed
-
- Tei C, Ling LH, Hodge DO, et al. New index of combined systolic and diastolic myocardial performance: a simple and reproducible measure of cardiac function--a study in normals and dilated cardiomyopathy. J Cardiol. 1995;26:357–366. - PubMed
-
- Bruch C, Schmermund A, Marin D, et al. Tei-index in patients with mild-to-moderate congestive heart failure. Eur Heart J. 2000;21:1888–1895. - PubMed
-
- Møller JE, Egstrup K, Køber L, Poulsen SH, Nyvad O, Torp-Pedersen C. Prognostic importance of systolic and diastolic function after acute myocardial infarction. Am Heart J. 2003;145:147–153. - PubMed
-
- Abd El Rahman MY, Hui W, Dsebissowa F, et al. Comparison of the tissue Doppler-derived left ventricular Tei index to that obtained by pulse Doppler in patients with congenital and acquired heart disease. Pediatr Cardiol. 2005;26:391–395. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

