A single dose of carbon monoxide intraperitoneal administration protects rat intestine from injury induced by lipopolysaccharide
- PMID: 20339960
- PMCID: PMC3006624
- DOI: 10.1007/s12192-010-0183-0
A single dose of carbon monoxide intraperitoneal administration protects rat intestine from injury induced by lipopolysaccharide
Abstract
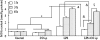
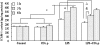
Treatment with inhaled carbon monoxide (CO) has been shown to ameliorate intestinal injury induced by lipopolysaccharide (LPS) or ischemia-reperfusion in experimental animals. We hypothesized that CO intraperitoneal administration (i.p) might provide similar protection against inhaled gas. In the present study, 1 h after intravenously receiving 5 mg/kg LPS, rats were exposed to either room air or 2 ml/kg of 250 ppm CO i.p for 1, 3, and 6 h. Intestinal tissues were collected to determine the levels of platelet activator factor (PAF), intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1), interleukin-10 (IL-10), maleic dialdehyde (MDA), cell apoptotic rate and the phosphorylated p38 mitogen activated protein kinase (MAPK), as well as myeloperoxidase (MPO) and superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity. After CO i.p, the increase of PAF, ICAM-1, MDA, MPO, and cell apoptosis rate induced by LPS was markedly reduced (P < 0.05 or 0.01), while the decrease of IL-10 and SOD was significantly increased (P < 0.05). Western blotting showed that the effects of CO i.p were mediated by p38 MAPK pathway. Thus, the results of our study show that CO i.p exerts potent protection against LPS induced injury to the intestine via anti-oxidant, anti-inflammation and anti-apoptosis, which may involve the p38 MAPK pathway.
Figures
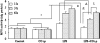

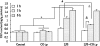
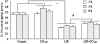
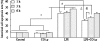


Similar articles
-
Protection of carbon monoxide intraperitoneal administration from rat intestine injury induced by lipopolysaccharide.Chin Med J (Engl). 2010 Apr 20;123(8):1039-46. Chin Med J (Engl). 2010. PMID: 20497711
-
[Effects of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase in protection of carbon monoxide against lipopolysaccharide induced rat small intestine injury].Zhongguo Ying Yong Sheng Li Xue Za Zhi. 2009 May;25(2):277-81. Zhongguo Ying Yong Sheng Li Xue Za Zhi. 2009. PMID: 21189571 Chinese.
-
Protection of carbon monoxide inhalation on lipopolysaccharide-induced multiple organ injury in rats.Chin Med Sci J. 2007 Sep;22(3):169-76. Chin Med Sci J. 2007. PMID: 17966165
-
Carbon monoxide inhalation protects lung from lipopolysaccharide-induced injury in rat.Sheng Li Xue Bao. 2006 Oct 25;58(5):483-9. Sheng Li Xue Bao. 2006. PMID: 17041734
-
[The mechanisms of carbon monoxide inhalation on the apoptosis of pulmonary cells in rats with acute lung injury induced by lipopolysaccharide].Zhonghua Jie He He Hu Xi Za Zhi. 2006 May;29(5):329-32. Zhonghua Jie He He Hu Xi Za Zhi. 2006. PMID: 16759493 Chinese.
Cited by
-
Salvianolic Acid B Regulates Oxidative Stress, Autophagy and Apoptosis against Cyclophosphamide-Induced Hepatic Injury in Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus).Animals (Basel). 2023 Jan 18;13(3):341. doi: 10.3390/ani13030341. Animals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36766230 Free PMC article.
-
Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells Combat Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Sepsis in Rats via Amendment of P38-MAPK Signaling Cascade.Inflammation. 2018 Mar;41(2):541-554. doi: 10.1007/s10753-017-0710-6. Inflammation. 2018. PMID: 29204871
-
Protective effect of dexmedetomidine against organ dysfunction in a two-hit model of hemorrhage/resuscitation and endotoxemia in rats.Braz J Med Biol Res. 2019 Feb 25;52(3):e7905. doi: 10.1590/1414-431X20187905. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2019. PMID: 30810621 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of the new synthetic vitamin E derivative ETS-GS on radiation enterocolitis symptoms in a rat model.Oncol Lett. 2013 Nov;6(5):1229-1233. doi: 10.3892/ol.2013.1581. Epub 2013 Sep 12. Oncol Lett. 2013. PMID: 24179500 Free PMC article.
-
CREG1 attenuates doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity by inhibiting the ferroptosis of cardiomyocytes.Redox Biol. 2024 Sep;75:103293. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2024.103293. Epub 2024 Jul 29. Redox Biol. 2024. PMID: 39094399 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bradbury CM, Markovina S, Wei SJ, Rene LM, Zoberi I, Horikoshi N, Gius D. Indomethacin-induced radiosensitization and inhibition of ionizing radiation-induced NF-kappaB activation in HeLa cells occur via a mechanism involving p38 MAP kinase. Cancer Res. 2001;61:7689–7696. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

