Dopaminergic regulation of dopamine D3 and D3nf receptor mRNA expression
- PMID: 20340170
- PMCID: PMC2888922
- DOI: 10.1002/syn.20770
Dopaminergic regulation of dopamine D3 and D3nf receptor mRNA expression
Abstract
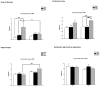
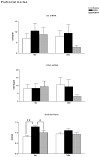
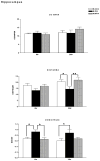
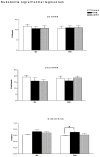
Dopamine D3 receptors have the highest dopamine affinity of all dopamine receptors, and may thereby regulate dopamine signaling mediated by volume transmission. Changes in D3 receptor isoform expression may alter D3 receptor function, however, little is known regarding coordination of D3 isoform expression in response to perturbations in dopaminergic stimulation. To determine the effects of dopamine receptor stimulation and blockade on D3 receptor alternative splicing, we determined D3 and D3nf isoform mRNA expression following treatment with the D3 receptor antagonist NGB 2904, and the indirect dopamine agonist amphetamine. Expression of tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) mRNA, the rate-limiting enzyme in dopamine synthesis, was also determined. The D3/D3nf mRNA expression ratio was increased in ventral striatum, prefrontal cortex, and hippocampus 6 h following D3 antagonist NGB 2904 treatment, and remained persistently elevated at 24 h in hippocampus and substantia nigra/ventral tegmentum. D3 mRNA decreased 65% and D3nf mRNA expression decreased 71% in prefrontal cortex 24 h following amphetamine treatment, however, these changes did not reach statistical significance. TH mRNA expression was unaffected by D3 antagonist NGB 2904, but was elevated by amphetamine in ventral striatum, hippocampus, and prefrontal cortex. These findings provide evidence for an adaptive response to altered D3 receptor stimulation involving changes in D3 receptor alternative splicing. Additionally, these data suggest D3 autoreceptor regulation of dopamine synthesis does not involve regulation of TH mRNA expression. Finally, the observation of regulated TH mRNA expression in dopamine terminal fields provides experimental support for the model of local control of mRNA expression in adaptation to synaptic activity.
Figures
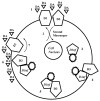
 represents the novel 55 amino acid carboxy-terminal tail D3nf sequence, resulting from the alternative splicing frame shift. 1), Drugs of abuse, stress, and psychiatric conditions including schizophrenia increase extracellular dopamine. 2) D1 and D3 receptor stimulation activate opposing intracellular signaling systems. D3 receptor has the highest dopamine affinity. Persistent D3 stimulation results in homeostatic mechanisms opposing receptor stimulation, including 3) increased D3nf expression. 4) D3nf and D3 dimerize, directing the D3/D3nf dimer 5) towards intracytoplasmic trafficking pools and removing D3 receptor from the synaptic membrane. 6) At the next elevated extracellular dopamine exposure D3 receptor is not available to bind dopamine. 7) The result is release of D3 receptor-mediated opposition to D1 receptor stimulation of adenylate cyclase activity.
represents the novel 55 amino acid carboxy-terminal tail D3nf sequence, resulting from the alternative splicing frame shift. 1), Drugs of abuse, stress, and psychiatric conditions including schizophrenia increase extracellular dopamine. 2) D1 and D3 receptor stimulation activate opposing intracellular signaling systems. D3 receptor has the highest dopamine affinity. Persistent D3 stimulation results in homeostatic mechanisms opposing receptor stimulation, including 3) increased D3nf expression. 4) D3nf and D3 dimerize, directing the D3/D3nf dimer 5) towards intracytoplasmic trafficking pools and removing D3 receptor from the synaptic membrane. 6) At the next elevated extracellular dopamine exposure D3 receptor is not available to bind dopamine. 7) The result is release of D3 receptor-mediated opposition to D1 receptor stimulation of adenylate cyclase activity.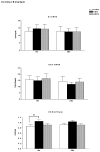
References
-
- Elmhurst JL, Xie Z, O’Dowd BF, George SR. The splice variant D3nf reduces ligand binding to the D3 dopamine receptor: evidence for heterooligomerization. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 2000;80:63–74. - PubMed
-
- Fedele E, Fontana G, Munari C, Cossu M, Raiteri M. Native human neocortex release-regulating dopamine D2 type autoreceptors are dopamine D2 subtype. Eur J Neurosci. 1999;11:2351–2358. - PubMed
-
- Fishburn CS, Belleli D, David C, Carmon S, Fuchs S. A novel short isoform of the D3 dopamine receptor generated by alternative splicing in the third cytoplasmic loop. J Biol Chem. 1993;268:5872–5878. - PubMed
-
- Goldstein M. Long- and short-term regulation of tyrosine hydroxylase. In: Bloom FE, Kupfer DJ, editors. Psychopharmacology: the Fourth Generation of Progress. New York: Raven Press; 1995. pp. 189–195.
-
- Gregory H, Taylor CL, Hopkins CR. Luteinizing hormone release from dissociated pituitary cells by dimerization of occupied LHRH receptors. Nature. 1982;300:269–271. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
