ER-β mediates 17β-estradiol attenuation of HIV-1 Tat-induced apoptotic signaling
- PMID: 20340172
- PMCID: PMC3428118
- DOI: 10.1002/syn.20793
ER-β mediates 17β-estradiol attenuation of HIV-1 Tat-induced apoptotic signaling
Abstract
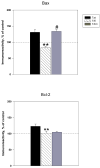
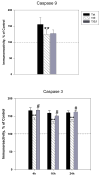
The protective actions of estrogen have been well evaluated in various models of neurodegeneration. These neuroprotective mechanisms may include a direct neuronal antiapoptotic effect as estrogen modulates actions of key regulators of the mitochondrial/intrinsic apoptotic cascade. We tested the ability of estrogen to protect against apoptotic signaling in cortical cell cultures exposed to Tat 1-86 (50 nM), and additionally, whether the beneficial actions of estrogen involved an estrogen receptor sensitive mechanism. We demonstrated that estrogen pretreatment significantly delayed Tat-induced cell death in primary cortical cultures. Pretreatment with 17β-estradiol (10 nM) attenuated the increased expression of antiapoptotic protein Bcl-2, proapoptotic protein Bax and activation of caspases linked to mitochondrial apoptotic pathway following Tat exposure. In addition, select components of apoptotic pathway signaling appear more sensitive to estrogen receptor (ER) activation, as the addition of ER antagonist ICI 182780 reversed estrogen downregulation of Bax and caspase 3, while estrogen effects on Tat-induced Bcl-2 and caspase 9 expression were maintained. Moreover, the addition of preferential ERα and ERβ antagonists (MPP dihydrochloride and PHTPP) indicated that estrogen effects on caspase 3 may be mediated by both receptor subtypes, whereas, was more involved in estrogen effects on Bax. Our data suggest that estrogen intervenes against HIV-1 Tat-induced cortical neuronal dysfunction via intersecting mitochondrial apoptotic pathway signaling in an ER-sensitive manner.
Figures






References
-
- Aksenov MY, Hasselrot U, Bansal Ak, et al. Oxidative damage induced by the injection of HIV-1 Tat protein in the rat striatum. Neurosci Lett. 2001;305:5–8. - PubMed
-
- Aksenov MY, Hasselrot U, Wu G, et al. Temporal relationships between HIV-1 Tat-induced neuronal degeneration, OX-42 immunoreactivity, reactive astrocytosis, and protein oxidation in the rat striatum. Brain Res. 2003;987:1–9. - PubMed
-
- Amantea D, Russo R, Bagetta G, Corasaniti MT. From clinical evidence to molecular mechanisms underlying neuroprotection afforded by estrogens. Pharmacol Res. 2005;52:119–132. - PubMed
-
- Ances BM, Ellis RJ. Dementia and neurocognitive disorders due to HIV-1 infection. Semin Neurol. 2007;27:86–92. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
