Effects of a novel arginine methyltransferase inhibitor on T-helper cell cytokine production
- PMID: 20345902
- PMCID: PMC2903848
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2010.07623.x
Effects of a novel arginine methyltransferase inhibitor on T-helper cell cytokine production
Abstract
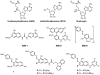
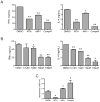
The protein arginine methyltransferase (PRMT) family of enzymes catalyzes the transfer of methyl groups from S-adenosylmethionine to the guanidino nitrogen atom of peptidylarginine to form monomethylarginine or dimethylarginine. We created several less polar analogs of the specific PRMT inhibitor arginine methylation inhibitor-1, and one such compound was found to have improved PRMT inhibitory activity over the parent molecule. The newly identified PRMT inhibitor modulated T-helper-cell function and thus may serve as a lead for further inhibitors useful for the treatment of immune-mediated disease.
Figures

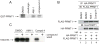
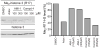

References
-
- Lin WJ, Gary JD, Yang MC, Clarke S, Herschman HR. The mammalian immediate-early TIS21 protein and the leukemia-associated BTG1 protein interact with a protein-arginine N-methyltransferase. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:15034–15044. - PubMed
-
- Bedford MT, Richard S. Arginine methylation an emerging regulator of protein function. Mol Cell. 2005;18:263–272. - PubMed
-
- Krause CD, Yang ZH, Kim YS, Lee JH, Cook JR, Pestka S. Protein arginine methyltransferases: Evolution and assessment of their pharmacological and therapeutic potential. Pharmacol Ther. 2007;113:50–87. - PubMed
-
- Lee DY, Ianculescu I, Purcell D, Zhang X, Cheng X, Stallcup MR. Surface-scanning mutational analysis of protein arginine methyltransferase 1: roles of specific amino acids in methyltransferase substrate specificity, oligomerization, and coactivator function. Mol Endocrinol. 2007;21:1381–1393. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

