A role for human endogenous retrovirus-K (HML-2) in rheumatoid arthritis: investigating mechanisms of pathogenesis
- PMID: 20345981
- PMCID: PMC2883104
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2010.04110.x
A role for human endogenous retrovirus-K (HML-2) in rheumatoid arthritis: investigating mechanisms of pathogenesis
Abstract
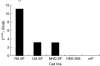
Human endogenous retroviruses (HERVs) are remnants of ancient retroviral infections within the human genome. These molecular fossils draw parallels with present-day exogenous retroviruses and have been linked previously with immunopathology within rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Mechanisms of pathogenesis for HERV-K in RA such as molecular mimicry were investigated. To clarify a role for HERVs in RA, potential autoantigens implicated in autoimmunity were scanned for sequence identity with retroviral epitopes. Short retroviral peptides modelling shared epitopes were synthesized, to survey anti-serum of RA patients and disease controls. A novel real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR) assay was also developed to quantify accurately levels of HERV-K (HML-2) gag expression, relative to normalized housekeeping gene expression. Both serological and molecular assays showed significant increases in HERV-K (HML-2) gag activity in RA patients, compared to disease controls. The real-time PCR assay identified significant up-regulation in HERV-K mRNA levels in RA patients compared to inflammatory and healthy controls. Exogenous viral protein expression and proinflammatory cytokines were also shown to exert modulatory effects over HERV-K (HML-2) transcription. From our data, it can be concluded that RA patients exhibited significantly elevated levels of HERV-K (HML-2) gag activity compared to controls. Additional factors influencing HERV activity within the synovium were also identified. The significant variation in RA patients, both serologically and transcriptionally, may be an indication that RA is an umbrella term for a number of separate disease entities, of which particular HERV polymorphisms may play a role in development.
Figures





References
-
- Lander ES, Linton LM, Birren B, et al. Initial sequencing and analysis of the human genome. Nature. 2001;409:860–921. - PubMed
-
- Boller K, Schonfeld K, Lischer S, et al. Human endogenous retrovirus HERV-K113 is capable of producing intact viral particles. J Gen Virol. 2008;89:567–72. - PubMed
-
- Michaels FH, Banks KL, Reitz MS., Jr Lessons from caprine and ovine retrovirus infections. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 1991;17:5–23. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

