Hypersensitivity reaction and acute immune-mediated thrombocytopenia from oxaliplatin: two case reports and a review of the literature
- PMID: 20346128
- PMCID: PMC2859393
- DOI: 10.1186/1756-8722-3-12
Hypersensitivity reaction and acute immune-mediated thrombocytopenia from oxaliplatin: two case reports and a review of the literature
Abstract
Background: Oxaliplatin is a platinum compound used in the treatment of gastrointestinal malignancies, including colorectal cancer. The incidence of hypersensitivity reaction in patients receiving oxaliplatin is approximately 15%, with severe reaction (grade 3 and 4) occurring in 2% of patients.
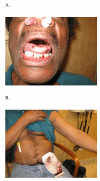
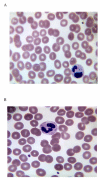
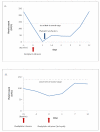
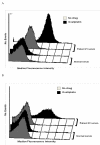
Case presentation: We report two patients with metastatic colorectal cancer who developed de novo hypersensitivity reaction and acute thrombocytopenia after oxaliplatin infusion. Both patients had oxaliplatin treatment several years before and exhibited hypersensitivity on the third dose of oxaliplatin in recent treatment. Oxaliplatin was discontinued when clinical reaction was identified. Both patients were confirmed to have strong oxaliplatin-induced IgG platelet-reactive antibodies. Both patients' thrombocytopenia resolved within two weeks after discontinuation of oxaliplatin. One patient had disease stabilization lasting for three months without chemotherapy. Both patients subsequently received other chemotherapeutic agents without evidence of hypersensitivity reaction or immune-mediated thrombocytopenia.
Conclusion: We recommend vigilant monitoring of complete blood count and signs and symptoms of bleeding after the occurrence of oxaliplatin-induced hypersensitivity to avoid serious complications of immune-mediated thrombocytopenia.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Oxaliplatin-Induced Immune-Mediated Thrombocytopenia: A Case Report.Cancer Res Treat. 2015 Oct;47(4):949-53. doi: 10.4143/crt.2014.052. Epub 2014 Oct 28. Cancer Res Treat. 2015. PMID: 25544580 Free PMC article.
-
Oxaliplatin-induced immune-mediated cytopenias: a case report and literature review.J Oncol Pharm Pract. 2015 Apr;21(2):148-56. doi: 10.1177/1078155213520262. Epub 2014 Feb 5. J Oncol Pharm Pract. 2015. PMID: 24500808 Review.
-
Acute immune-mediated thrombocytopenia due to oxaliplatin administration: a case report.Tumori. 2010 Jan-Feb;96(1):154-6. doi: 10.1177/030089161009600125. Tumori. 2010. PMID: 20437874
-
Oxaliplatin-induced acute thrombocytopenia: a case report and review of the literature.Intern Med. 2013;52(5):611-5. doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.52.8933. Epub 2013 Mar 1. Intern Med. 2013. PMID: 23448774 Review.
-
Clinical features of hypersensitivity reactions to oxaliplatin: a 10-year experience.Oncology. 2009;76(1):36-41. doi: 10.1159/000178163. Epub 2008 Nov 26. Oncology. 2009. PMID: 19033714
Cited by
-
Acute Immune-Mediated Thrombocytopenia due to Oxaliplatin and Irinotecan Therapy.Case Rep Oncol Med. 2019 Nov 4;2019:4314797. doi: 10.1155/2019/4314797. eCollection 2019. Case Rep Oncol Med. 2019. PMID: 31781443 Free PMC article.
-
A 39-year-old female patient with metastatic rectal cancer develops thrombocytopenia.Gastrointest Cancer Res. 2014 Mar;7(2):55-8. Gastrointest Cancer Res. 2014. PMID: 24799972 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Management of hypersensitivity to platinum- and taxane-based chemotherapy: cepo review and clinical recommendations.Curr Oncol. 2014 Aug;21(4):e630-41. doi: 10.3747/co.21.1966. Curr Oncol. 2014. PMID: 25089112 Free PMC article.
-
Hypersensitivity reactions associated with platinum antineoplastic agents: a systematic review.Met Based Drugs. 2010;2010:207084. doi: 10.1155/2010/207084. Epub 2010 Sep 20. Met Based Drugs. 2010. PMID: 20886011 Free PMC article.
-
Allergy in Cancer Care: Antineoplastic Therapy-Induced Hypersensitivity Reactions.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 15;24(4):3886. doi: 10.3390/ijms24043886. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36835299 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Goldberg RM, Sargent DJ, Morton RF, Fuchs CS, Ramanathan RK, Williamson SK, Findlay BP, Pitot HC, Alberts SR. A randomized controlled trial of fluorouracil plus leucovorin, irinotecan, and oxaliplatin combinations in patients with previously untreated metastatic colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2004;22(1):23–30. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2004.09.046. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

