MicroRNA expression after ionizing radiation in human endothelial cells
- PMID: 20346162
- PMCID: PMC2859352
- DOI: 10.1186/1748-717X-5-25
MicroRNA expression after ionizing radiation in human endothelial cells
Abstract
Background: Endothelial cells (EC) in tumor and normal tissue constitute critical radiotherapy targets. MicroRNAs have emerged as master switchers of the cellular transcriptome. Here, we seek to investigate the role of miRNAs in primary human dermal microvascular endothelial cells (HDMEC) after ionizing radiation.
Methods: The microRNA status in HDMEC after 2 Gy radiation treatment was measured using oligo-microarrays covering 361 miRNAs. To functionally analyze the role of radiation-induced differentially regulated miRNAs, cells were transfected with miRNA precursor or inhibitor constructs. Clonogenic survival and proliferation assays were performed.
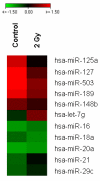
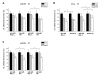
Results: Radiation up-regulated miRNA expression levels included let-7g, miR-16, miR-20a, miR-21 and miR-29c, while miR-18a, miR-125a, miR-127, miR-148b, miR-189 and miR-503 were down-regulated. We found that overexpression or inhibition of let-7g, miR-189, and miR-20a markedly influenced clonogenic survival and cell proliferation per se. Notably, the radiosensitivity of HDMEC was significantly influenced by differential expression of miR-125a, -127, -189, and let-7g. While miR-125a and miR-189 had a radioprotective effect, miR-127 and let-7g enhanced radiosensitivity in human endothelial cells.
Conclusion: Our data show that ionizing radiation changes microRNA levels in human endothelial cells and, moreover, exerts biological effects on cell growth and clonogenicity as validated in functional assays. The data also suggest that the miRNAs which are differentially expressed after radiation modulate the intrinsic radiosensitivity of endothelial cells in subsequent irradiations. This indicates that miRNAs are part of the innate response mechanism of the endothelium to radiation.
Figures
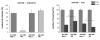
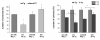
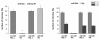
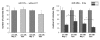
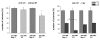
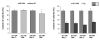
Similar articles
-
MicroRNA-148b enhances the radiosensitivity of non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma cells by promoting radiation-induced apoptosis.J Radiat Res. 2012 Jul;53(4):516-25. doi: 10.1093/jrr/rrs002. Epub 2012 Jun 6. J Radiat Res. 2012. PMID: 22843616 Free PMC article.
-
miR-9 and let-7g enhance the sensitivity to ionizing radiation by suppression of NFκB1.Exp Mol Med. 2011 May 31;43(5):298-304. doi: 10.3858/emm.2011.43.5.031. Exp Mol Med. 2011. PMID: 21464588 Free PMC article.
-
Peritoneal fluid modifies the microRNA expression profile in endometrial and endometriotic cells from women with endometriosis.Hum Reprod. 2015 Oct;30(10):2292-302. doi: 10.1093/humrep/dev204. Epub 2015 Aug 25. Hum Reprod. 2015. PMID: 26307093
-
Embryonic stem cell microRNAs: defining factors in induced pluripotent (iPS) and cancer (CSC) stem cells?Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2009 Sep;4(3):168-77. doi: 10.2174/157488809789057400. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2009. PMID: 19492978 Review.
-
Epigenetic interventions increase the radiation sensitivity of cancer cells.Curr Pharm Des. 2014;20(11):1857-65. doi: 10.2174/13816128113199990529. Curr Pharm Des. 2014. PMID: 23888958 Review.
Cited by
-
Gamma-Tocotrienol Modulates Radiation-Induced MicroRNA Expression in Mouse Spleen.Radiat Res. 2016 May;185(5):485-95. doi: 10.1667/RR14248.1. Epub 2016 Apr 29. Radiat Res. 2016. PMID: 27128741 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of a novel peptide Ac-SDKP in radiation-induced coronary endothelial damage and resting myocardial blood flow.Cardiooncology. 2018;4:8. doi: 10.1186/s40959-018-0034-1. Epub 2018 Dec 18. Cardiooncology. 2018. PMID: 31057947 Free PMC article.
-
miRNA-148b regulates radioresistance in non-small lung cancer cells via regulation of MutL homologue 1.Biosci Rep. 2016 Jun 30;36(3):e00354. doi: 10.1042/BSR20150300. Print 2016 Jul. Biosci Rep. 2016. Retraction in: Biosci Rep. 2021 Apr 30;41(4):BSR-20150300_RET. doi: 10.1042/BSR-20150300_RET. PMID: 26759383 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Radiobiological Studies of Microvascular Damage through In Vitro Models: A Methodological Perspective.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Mar 9;13(5):1182. doi: 10.3390/cancers13051182. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33803333 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Differential miRNA expression profiling reveals miR-205-3p to be a potential radiosensitizer for low- dose ionizing radiation in DLD-1 cells.Oncotarget. 2018 May 29;9(41):26387-26405. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.25405. eCollection 2018 May 29. Oncotarget. 2018. PMID: 29899866 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mendell JT. MicroRNAs: Critical regulators of development, cellular physiology and malignancy. Cell Cycle. 2005;4:1179–1184. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

