Toll-like receptors in ocular surface disease
- PMID: 20346359
- PMCID: PMC2905230
- DOI: 10.1016/j.exer.2010.03.012
Toll-like receptors in ocular surface disease
Abstract
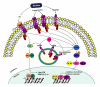
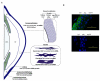
The ability of the ocular surface to mount an immune response is in part attributed to a family of proteins called toll-like receptors (TLRs). The latter are evolutionary conserved receptors that recognize and respond to various microbes and endogenous ligands. In addition to their recognition function, TLR activation triggers a complex signal transduction cascade that induces the production of inflammatory cytokines and co-stimulatory molecules, thus initiating innate and adaptive immunity. Toll-like receptor expression at the ocular surface is modulated during infection (e.g. Herpes simplex, bacterial keratitis and fungal keratitis) as well as during various inflammatory conditions (allergic conjunctivitis and dry-eye syndrome). Here recent findings regarding TLR expression and their involvement in various ocular surface diseases are discussed.
Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Figures
References
-
- Afonso AA, Obrin L, Monroy DC, et al. Tear fluid gelatinase B activity correlates with IL-1alpha concentration and fluorescein clearance in ocular rosacea. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1999;40:2506–2512. - PubMed
-
- Albiger B, Dahlberg S, Henriques-Normark B, et al. Role of the innate immune system in host defense against bacterial infections: Focus on Toll-like receptors. J Int Med. 2007;261:511–528. - PubMed
-
- Alexopoulou L, Holt AC, Medzhitov R, et al. Recognition of double-stranded RNA and activation of NF-kappaB by Toll-like receptor 3. Nature. 2001;413:732–738. - PubMed
-
- Bauer S, Hangel D, Yu P. Immunobiology of toll-like receptors in allergic disease. Immunobiol. 2007;212:521–533. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

