Comparing body composition assessment tests in long-term hemodialysis patients
- PMID: 20346558
- PMCID: PMC3175362
- DOI: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2009.12.031
Comparing body composition assessment tests in long-term hemodialysis patients
Abstract
Background: Protein-energy wasting is common in chronic kidney disease and is associated with decreases in body muscle and fat stores and poor outcomes. The accuracy and reliability of field methods to measure body composition is unknown in this population.
Study design: Cross-sectional observational study.
Setting & participants: 118 maintenance hemodialysis patients were seen at the General Clinical Research Center at Harbor-UCLA Medical Center, Torrance, CA.
Index tests: Triceps skinfold, near-infrared interactance, and bioelectrical impedance analysis using the Segal, Kushner, and Lukaski equations.
Reference test: Dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry (DEXA).
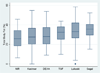
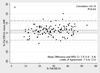
Results: Participants (42% women, 52% with diabetes, 40% African Americans, and 38% Hispanics) were aged 49.4 +/- 11.5 (mean +/- SD) years, and had undergone dialysis therapy for 41.1 +/- 32.9 months. Body mass index was 27.0 +/- 6.0 kg/m(2). Using DEXA as the reference test, the bioelectrical impedance analysis-Kushner equation, triceps skinfold, and near-infrared interactance were most accurate of the index tests in estimating total-body fat percentage, whereas bioelectrical impedance analysis-Segal equation and bioelectrical impedance analysis-Lukaski equation overestimated total body fat percentage. Bland-Altman analyses and difference plots showed that bioelectrical impedance analysis-Kushner and near-infrared interactance were most similar to the reference test. Bioelectrical impedance analysis-Kushner, triceps skinfold, and near-infrared interactance had the smallest mean differences from DEXA, especially in women (1.6%, 0.7%, and 1.2%, respectively). Similar results were observed in African American participants (n = 47).
Limitations: Measurements were performed 1 day after a hemodialysis treatment, leading to more fluid retention, which may have affected the reference and index tests differently.
Conclusions: Using DEXA as the reference test, both near-infrared interactance and bioelectrical impedance analysis-Kushner method yield more consistent estimates of total body fat percentage in maintenance hemodialysis patients compared with the other index tests. Near-infrared interactance is not affected by skin color. Field methods with portable devices may provide adequate precision.
Copyright 2010 National Kidney Foundation, Inc. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Comparison of three methods for the determination of body fat in patients on long-term hemodialysis therapy.J Am Diet Assoc. 2003 Feb;103(2):195-9. doi: 10.1053/jada.2003.50024. J Am Diet Assoc. 2003. PMID: 12589325
-
Novel equations to estimate lean body mass in maintenance hemodialysis patients.Am J Kidney Dis. 2011 Jan;57(1):130-9. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2010.10.003. Am J Kidney Dis. 2011. PMID: 21184920 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of Body Mass Index, Skinfold Thickness, and Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis With Dual-Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry in Hemodialysis Patients.Nutr Clin Pract. 2020 Dec;35(6):1021-1028. doi: 10.1002/ncp.10481. Epub 2020 Mar 5. Nutr Clin Pract. 2020. PMID: 32141138
-
Use of bioelectric impedance analysis and dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry for monitoring the nutritional status of dialysis patients.ASAIO J. 1997 May-Jun;43(3):256-60. ASAIO J. 1997. PMID: 9152505 Review.
-
Body fluid volumes measurements by impedance: A review of bioimpedance spectroscopy (BIS) and bioimpedance analysis (BIA) methods.Med Eng Phys. 2008 Dec;30(10):1257-69. doi: 10.1016/j.medengphy.2008.06.009. Epub 2008 Aug 3. Med Eng Phys. 2008. PMID: 18676172 Review.
Cited by
-
Comparison analysis of nutritional scores for serial monitoring of nutritional status in hemodialysis patients.Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2013 Mar;8(3):443-51. doi: 10.2215/CJN.04980512. Epub 2013 Feb 14. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2013. PMID: 23411424 Free PMC article.
-
Agreement of Single-Frequency Electrical Bioimpedance in the Evaluation of Fat Free Mass and Fat Mass in Peritoneal Dialysis Patients.Front Nutr. 2021 May 31;8:686513. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2021.686513. eCollection 2021. Front Nutr. 2021. PMID: 34136524 Free PMC article.
-
A comparison of novel and commonly-used indices of insulin sensitivity in African American chronic hemodialysis patients.Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2011 Apr;6(4):767-74. doi: 10.2215/CJN.08070910. Epub 2011 Mar 24. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2011. PMID: 21441124 Free PMC article.
-
Body Fat in Children with Chronic Kidney Disease - A Comparative Study of Bio-impedance Analysis with Dual Energy X-ray Absorptiometry.Indian J Nephrol. 2021 Jan-Feb;31(1):39-42. doi: 10.4103/ijn.IJN_368_19. Epub 2020 Nov 7. Indian J Nephrol. 2021. PMID: 33994686 Free PMC article.
-
Mid-arm muscle circumference and quality of life and survival in maintenance hemodialysis patients.Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2010 Dec;5(12):2258-68. doi: 10.2215/CJN.02080310. Epub 2010 Oct 14. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2010. PMID: 20947789 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fouque D, Kalantar-Zadeh K, Kopple J, et al. A proposed nomenclature and diagnostic criteria for protein-energy wasting in acute and chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2008;73:391–398. - PubMed
-
- Kalantar-Zadeh K, Kilpatrick RD, Kuwae N, et al. Revisiting mortality predictability of serum albumin in the dialysis population: time dependency, longitudinal changes and population-attributable fraction. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2005;20:1880–1888. - PubMed

