The effects of the dopamine D2 agonist sumanirole on prepulse inhibition in rats
- PMID: 20346635
- PMCID: PMC2864324
- DOI: 10.1016/j.euroneuro.2010.02.011
The effects of the dopamine D2 agonist sumanirole on prepulse inhibition in rats
Abstract
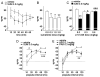
Dopamine agonists reduce prepulse inhibition (PPI) of startle in rats. While it is used to predict antipsychotic efficacy, the specific receptor subtypes mediating this effect of dopamine agonists remain unclear. We characterized the effects of sumanirole, a highly selective D2 agonist, on PPI in rats. Sumanirole decreased PPI at 60-120 ms prepulse intervals, and increased PPI at 10-20 ms intervals. PPI deficits were antagonized by low doses of the preferential D2 antagonist L741626, supporting a D2 mechanism of action. Sumanirole is a valuable tool for parsing the role of dopamine receptor subtypes in the regulation of PPI.
2010 Elsevier B.V. and ECNP. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Chang WL, Saint Marie RL, Miller E, Weber M, Swerdlow NR. Effects of the D3/D2 agonist, pramipexole, on sensorimotor gating and nucleus accumbens signaling in the rat. Biol Psychiatry. 2009;65:76s.
-
- Cussac D, Newman-Tancredi A, Sezgin L, Millan MJ. The novel antagonist, S33084, and GR218,231 interact selectively with cloned and native, rat dopamine D(3) receptors as compared with native, rat dopamine D(2) receptors. Eur J Pharmacol. 2000;394:47–50. - PubMed
-
- de Paulis T. Sumanirole Pharmacia. Curr Opin Investig Drugs. 2003;4:77–82. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

