Odor information processing by the olfactory bulb analyzed in gene-targeted mice
- PMID: 20346765
- PMCID: PMC2901914
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2010.02.011
Odor information processing by the olfactory bulb analyzed in gene-targeted mice
Abstract
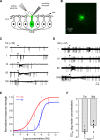
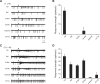
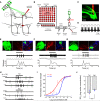
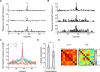
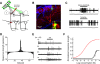
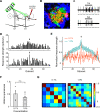
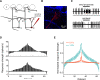
In mammals, olfactory sensory neurons (OSNs) expressing a specific odorant receptor (OR) gene project with precise stereotypy onto mitral/tufted (M/T) cells in the main olfactory bulb (MOB). It remains challenging to understand how incoming olfactory signals are transformed into outputs of M/T cells. By recording from OSNs expressing mouse I7 receptor and their postsynaptic neurons in the bulb, we found that I7 OSNs and their corresponding M/T cells exhibit similarly selective tuning profiles at low concentrations. Increasing the concentration significantly reduces response selectivity for both OSNs and M/T cells, although the tuning curve of M/T cells remains comparatively narrow. By contrast, interneurons in the MOB are broadly tuned, and blocking GABAergic neurotransmission reduces selectivity of M/T cells at high odorant concentrations. Our results indicate that olfactory information carried by an OR is channeled to its corresponding M/T cells and support the role of lateral inhibition via interneurons in sharpening the tuning of M/T cells.
(c) 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Araneda RC, Kini AD, Firestein S. The molecular receptive range of an odorant receptor. Nat. Neurosci. 2000;3:1248–1255. - PubMed
-
- Aungst JL, Heyward PM, Puche AC, Karnup SV, Hayar A, Szabo G, Shipley MT. Centre-surround inhibition among olfactory bulb glomeruli. Nature. 2003;426:623–629. - PubMed
-
- Bathellier B, Buhl DL, Accolla R, Carleton A. Dynamic ensemble odor coding in the mammalian olfactory bulb: sensory information at different timescales. Neuron. 2008;57:586–598. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

