Alan [corrected] N. Epstein award: Intracellular signaling and ingestive behaviors
- PMID: 20346964
- PMCID: PMC2886159
- DOI: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2010.03.012
Alan [corrected] N. Epstein award: Intracellular signaling and ingestive behaviors
Erratum in
- Physiol Behav. 2012 Feb 1;105(3):899
Abstract
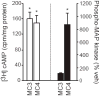
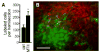
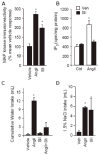
Understanding the role of intracellular signaling pathways in ingestive behavior is a challenging problem in behavioral neuroscience. This review summarizes work conducted on two systems with the aim of identifying intracellular events that relate to food and fluid intake. The first set of experiments focused on melanocortin receptors and their ability to signal through members of the mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase family. The second set of experiments focused on the role of intracellular signaling pathways in water and saline intakes that are stimulated by angiotensin II (AngII). The initial findings in each line of research have been extended by subsequent research that is discussed in turn. The paper represents an invited review by a symposium, award winner or keynote speaker at the Society for the Study of Ingestive Behavior [SSIB] Annual Meeting in Portland, July 2009.
2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The functional architecture of dehydration-anorexia.Physiol Behav. 2010 Jul 14;100(5):472-7. doi: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2010.04.010. Epub 2010 Apr 23. Physiol Behav. 2010. PMID: 20399797 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Preference or fat? Revisiting opioid effects on food intake.Physiol Behav. 2010 Jul 14;100(5):429-37. doi: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2010.02.027. Epub 2010 Mar 4. Physiol Behav. 2010. PMID: 20211638 Free PMC article. Review.
-
From mindless eating to mindlessly eating better.Physiol Behav. 2010 Jul 14;100(5):454-63. doi: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2010.05.003. Epub 2010 May 12. Physiol Behav. 2010. PMID: 20470810 Review.
-
Angiotensin II stimulates water and NaCl intake through separate cell signalling pathways in rats.Exp Physiol. 2009 Jan;94(1):130-7. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.2008.044446. Epub 2008 Aug 22. Exp Physiol. 2009. PMID: 18723579 Free PMC article.
-
Divergent behavioral roles of angiotensin receptor intracellular signaling cascades.Endocrinology. 2005 Dec;146(12):5552-60. doi: 10.1210/en.2005-0774. Epub 2005 Aug 25. Endocrinology. 2005. PMID: 16123155
Cited by
-
Mitogen-activated protein kinase is required for the behavioural desensitization that occurs after repeated injections of angiotensin II.Exp Physiol. 2012 Dec;97(12):1305-14. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.2012.065771. Epub 2012 May 11. Exp Physiol. 2012. PMID: 22581747 Free PMC article.
-
The brain renin-angiotensin system: a diversity of functions and implications for CNS diseases.Pflugers Arch. 2013 Jan;465(1):133-51. doi: 10.1007/s00424-012-1102-2. Epub 2012 Apr 26. Pflugers Arch. 2013. PMID: 22535332 Review.
-
Angiotensin II (de)sensitization: Fluid intake studies with implications for cardiovascular control.Physiol Behav. 2016 Aug 1;162:141-6. doi: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2016.01.020. Epub 2016 Jan 19. Physiol Behav. 2016. PMID: 26801390 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Acute repeated intracerebroventricular injections of angiotensin II reduce agonist and antagonist radioligand binding in the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus and median preoptic nucleus in the rat brain.Brain Res. 2014 Oct 2;1583:132-40. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2014.07.053. Epub 2014 Aug 7. Brain Res. 2014. PMID: 25108041 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zhang Y, Proenca R, Maffei M, Barone M, Leopold L, Friedman JM. Positional cloning of the mouse obese gene and its human homologue. Nature. 1994;372:425–32. - PubMed
-
- McKinley MJ, McAllen RM, Davern P, Giles ME, Penschow J, Sunn N, Uschakov A, Oldfield BJ. The sensory circumventricular organs of the mammalian brain. Adv Anat Embryol Cell Biol. 2003;172:1–127. - PubMed
-
- Johnson AK. The sensory psychobiology of thirst and salt appetite. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2007;39:1388–400. - PubMed
-
- Daniels D, Fluharty SJ. Neuroendocrinology of Body Fluid Homeostasis. In: Pfaff DW, Arnold AP, Fahrbach SE, Etgen AM, Rubin RT, editors. Hormones, Brain and Behavior, Second Edition. San Diego: Academic Press; 2009. pp. 259–288.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

