Alan [corrected] N. Epstein award: Intracellular signaling and ingestive behaviors
- PMID: 20346964
- PMCID: PMC2886159
- DOI: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2010.03.012
Alan [corrected] N. Epstein award: Intracellular signaling and ingestive behaviors
Erratum in
- Physiol Behav. 2012 Feb 1;105(3):899
Abstract
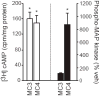
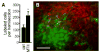
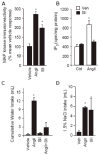
Understanding the role of intracellular signaling pathways in ingestive behavior is a challenging problem in behavioral neuroscience. This review summarizes work conducted on two systems with the aim of identifying intracellular events that relate to food and fluid intake. The first set of experiments focused on melanocortin receptors and their ability to signal through members of the mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase family. The second set of experiments focused on the role of intracellular signaling pathways in water and saline intakes that are stimulated by angiotensin II (AngII). The initial findings in each line of research have been extended by subsequent research that is discussed in turn. The paper represents an invited review by a symposium, award winner or keynote speaker at the Society for the Study of Ingestive Behavior [SSIB] Annual Meeting in Portland, July 2009.
2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Zhang Y, Proenca R, Maffei M, Barone M, Leopold L, Friedman JM. Positional cloning of the mouse obese gene and its human homologue. Nature. 1994;372:425–32. - PubMed
-
- McKinley MJ, McAllen RM, Davern P, Giles ME, Penschow J, Sunn N, Uschakov A, Oldfield BJ. The sensory circumventricular organs of the mammalian brain. Adv Anat Embryol Cell Biol. 2003;172:1–127. - PubMed
-
- Johnson AK. The sensory psychobiology of thirst and salt appetite. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2007;39:1388–400. - PubMed
-
- Daniels D, Fluharty SJ. Neuroendocrinology of Body Fluid Homeostasis. In: Pfaff DW, Arnold AP, Fahrbach SE, Etgen AM, Rubin RT, editors. Hormones, Brain and Behavior, Second Edition. San Diego: Academic Press; 2009. pp. 259–288.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

